Transport Canada released the final ELD Mandate rules through the Canada Gazette on June 13, 2019, which came into effect on June 12, 2021, and will be fully enforced beginning January 1, 2023. While Canada ELD rules have set the clock ticking for commercial vehicle owners to switch to a certified ELD, it has also led to several points of confusion, including the similarities and differences between U.S. and Canada ELD Mandate rules and its implications for carriers operating in both countries.
This complete guide on Canada ELD Mandate rules will discuss all the crucial factors related to the final rule issued by Transport Canada.
A Brief Overview of Canada ELD Mandate Rules
Canadian ELD Mandate rules will make it obligatory for all commercial vehicle drivers to record hours of service through registered electronic logging devices. An original compliance extension of one year was established by Transport Canada for progressive enforcement, which was later extended by six months so that papers log will not be accepted from January 1, 2023 onwards. Any commercial vehicle owner or fleet carrier failing to comply with these regulations by that date will be penalized.
Canada ELD rules have been issued by Transport Canada to increase road safety and vehicle security. The ELD Mandate regulations also facilitate better tracking and managing of commercial vehicles saving millions on paperwork and manual labor.
Canada and U.S. ELD Mandates
ELD Mandate rules published by Transport Canada and FMCSA in Canada and the U.S. respectively have many common regulations, but there are a few differences too. Take a quick look at the key similarities and differences between U.S. and Canada ELD rules.
Similarities between United States and Canada ELD Mandate Rules
These common factors between the United States and Canada elog regulations will help fleets stay compliant by using a single electronic logbook that fulfills the criteria of both transport authorities.
- Driving status. The device must automatically detect when the vehicle travels at a speed of 8km/hr or more and display “driving” as the duty status.
- Change of status after 5-minute pause. After the vehicle has stopped for 5 minutes, the electronic logbook automatically asks if the driver wants to change the status to “on duty” instead of “driving”.
- Yard-move mode. To avoid changing the status to “off duty” the driver must set it on “yard mode” when the speed drops below 8 km/ hour while driving inside a yard.
- Unassigned driving time. The device must request that unassigned driving time be claimed by a driver.
- Manage logbook. Drivers are allowed to edit, manage, and annotate logbook records only after they are registered to the ELD.
- Driving status cannot be changed. The driver is allowed to edit non-driving duty statuses, but driving time is recorded directly from the engine and cannot be modified.
Differences between United States and Canada ELD Mandate Rules
While the ELD Mandate rules of both countries are similar, there are also some differences that carriers should take into account. Let’s take a look at them:
- Hours of personal conveyance. Personal conveyance hours are allotted to the driver by the carriers when the vehicle is used in non-working hours. For instance, the driver can drive the vehicle to a garage or lodging. The U.S. ELD mandate has no limitation on time and distance on personal conveyance whereas Canada ELD rules have strictly set it to 75 kilometers (50 miles).
- Certification. The final rule of both Canada and the U.S. mandate has made it compulsory to use only registered electronic logbooks for recording HOS. The difference is, the United States has allowed manufacturers to self-register their device if it meets all FMCSA criteria, while Transport Canada has stated that all electronic logbooks must be certified by approved third-party agencies.
- Recording hours of service. The U.S. mandate allows truckers a 30-minute break after driving for 8 consecutive hours. Transport Canada has fixed a 16-hour window for shifts, which also include 2 off-duty hours.
- HOS reporting. In the U.S. the HOS information is directly transferred to the data-repository or ERODS, whereas in Canada HOS records are directly reported to the officer.
- No grandfather clause. While the U.S. mandate gave 2 extra years for carriers using ERDs to switch to ELDs, Canada’s ELD rules have no such provision. Transport Canada eliminated the grandfather clause asking truckers to replace ERDs with ELDs within the progressive enforcement period.
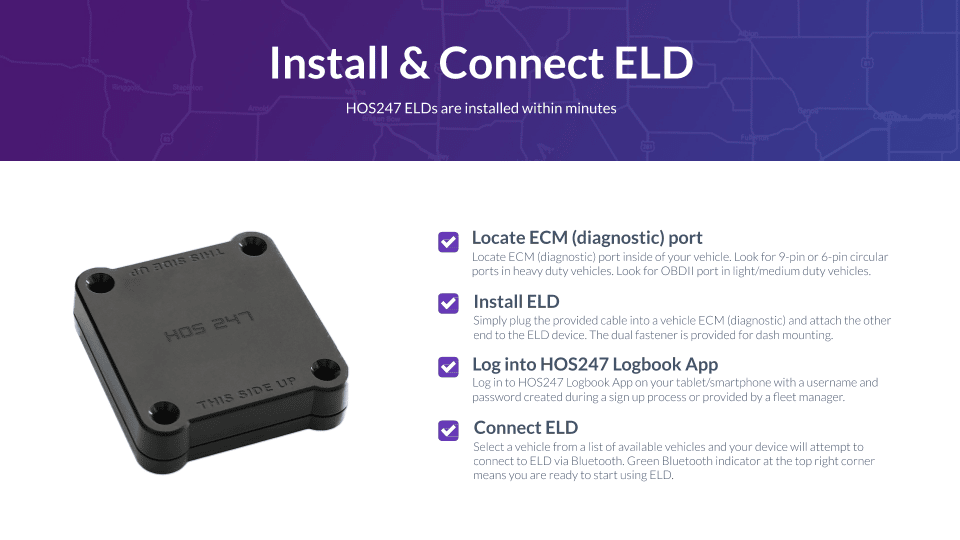
Uses of a Certified ELD
It is important for carriers and drivers to understand the ELD requirements to choose the right device. An electronic logging device or ELD is more than just a logbook; it is a tool that helps improve the productivity and security of fleets. Check out the beneficial uses of a certified logbook to understand its importance in road safety and fleet management.
- Improved road safety. A certified elog tracks the speed of the vehicle and alerts the carrier company in case of over-speeding and improper cornering. It also has notifications in case any fault is detected in vehicle diagnostics. All these features help increase road safety thereby minimizing accidents and vehicle break-downs.
- Monitoring driver behavior:.The device automatically records the HOS reducing driver idling time, personal usage of the vehicle, or vehicle usage during off-duty hours.
- Simplifying fleet management. A certified elog will save fleet companies from maintaining loads of logbook data.
Carriers Affected by Canadian ELD Mandate Rules
The final rule issued by Transport Canada applies to 157,500 commercial vehicles used for extra-provincial transportation. Vehicles operating in extra-provincial areas including local activities come under federal jurisdiction. All vehicles under federal jurisdiction must comply with the Canada ELD rules.
Exemptions to Canada ELD Rules
Vehicles, drivers and carriers can be exempt from using electronic logbooks according to the criteria set by Transport Canada, including:
- Vehicles operating on a special permit issued by a territorial or provincial director.
- Carriers granted a statutory exemption.
- Commercial vehicles operating under a rental agreement for a period under 30-days.
- Vehicle models manufactured before the year 2000.
- Drivers operating within a radius of 160 km from its home terminal (these vehicles are not required to maintain a logbook).
Benefits of Using HOS247 ELD
HOS247 is an industry leader in manufacturing registered ELDs that are accepted by both Transport Canada and FMCSA. HOS247 has a team of expert professionals who understand what ELD requirements are to help our clients stay compliant and productive. HOS247 has developed a reliable client base, ranging owner-operators and large carriers, by providing advanced electronic logbooks with the most flexible plans.
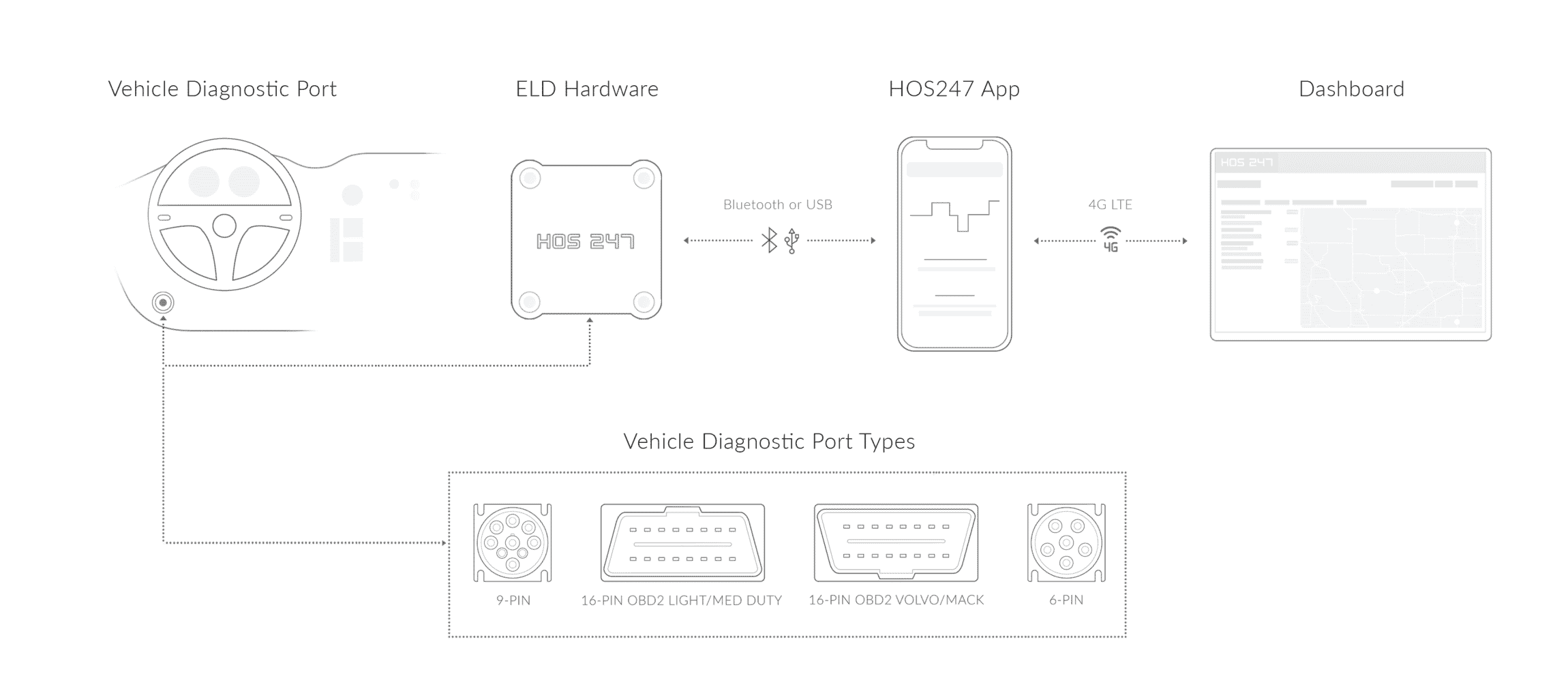
Check out the features and benefits of HOS247:
- Reliable hardware: HOS247 elog devices are durable and can be installed in minutes to start operating immediately. The device can be operated via Bluetooth using any smartphone or tablet.
- Easy to manage/edit logs: Edit and manage logs and DVIRs with a few clicks. Reports can be accessed instantly by carrier companies through the portal, via 4G network, and by drivers and roadside officials.
- Automated IFTA mileage: HOS247 logbooks are designed to automatically calculate IFTA state mileage. This prevents human error and avoids audit risks.
- Real-time GPS: All HOS247 logbooks are available with real-time GPS tracking. This helps increase the safety of the driver and vehicle. The GPS tracker helps carrier companies track the location of every truck in the fleet for faster dispatch. Real-time GPS tracking notifies the company if the vehicle is driven after working hours. The device also uses geofencing to alert the company in case the vehicle is driven in an unregistered area.
- Monitor vehicle diagnostics: The app keeps track of vehicle diagnostics and alerts the driver in case a fault or error is detected in the vehicle. It also notifies the company with special fault codes about the status of the error detected. This features allows fleet managers to stay ahead of vehicles’ maintenance needs and saves time preventing unnecessary delays.
- Stay compliant: The automated recording of driver logs and HOS eliminates all kinds of human error to stay compliant to Transport policies.
- Active customer-support team: HOS247 offers assistance to customers Monday through Sunday in four different languages: English, Russian, Spanish, and Polish. The company has a dedicated team of experts to guide customers on optimum utilization of the device to maximize profit with enhanced fleet operation.
- Flexible plan: HOS247 offers flexible plans to suit the requirements of carrier companies as well as individual owners. Whether it is for one truck or a fleet, HOS247 has a solution for every need.
- Free trial period: HOS247 provides a 14-day free trial period for all ELDs. The client does not need to enter into any contracts or submit any financial details to request a demo. It also comes with a free return policy if the client is not satisfied with the service.
The deadline for the ELD Mandate rules to be enforced by Transport Canada is getting closer. As Transport Canada has made it mandatory to get every ELD certified by third-party agencies, carrier companies in Canada are left with fewer options than their counterparts un the United Stated. Additionally, there is no grandfather clause to extend the period in the Canadian ELD mandate. Switching over to a certified logbook will save penalties and increase fleet efficiency. Relying on an already registered and trusted supplier like HOS247 ahead of time might save compliance issues once the progressive enforcement period is over. HOS247 ELDs have been trusted by fleet companies and individual owners for years because of their reliability, useful features and top-rated user support.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











The Canadian ELD Mandate is a fact of life for most drivers and trucking companies. This article presents some guidelines on how to choose ELD devices, how to stay on top of a trucking company and driver regulatory needs, who

Electronic logging devices (ELDs) have revolutionized the trucking industry, providing a more accurate, efficient, and secure way for truckers to record their hours of service (HOS) and ensure compliance with federal regulations. Transport Canada mandates the use of ELDs for

HOS247 – An Industry Leader HOS247 is an industry leader providing elogs apps for the transportation industry. There are many reasons why drivers and fleet managers choose HOS247 when in search of an Transport Canada electronic logging app solution. Benefits
