As the trucking industry in Canada advances, the adoption of electronic logging devices (ELDs) is reshaping how commercial motor vehicle (CMV) drivers maintain their records of duty status (RODS). This article sheds light on key differences between paper and electronic CMV logbooks, ELD applicability for different vehicle types, intraprovincial requirements, and the advantages of HOS247 as a leading ELD provider.
CMV Logbook Types
According to Transport Canada, a paper logbook refers to a physical paper-based record used by commercial vehicle drivers to manually document their hours of service (HOS) activities. For decades, paper logs were used to keep track of drivers’ working hours.
This changed with the implementation of the mandate, and now most cmv driver hours of service are recorded using electronic logs. While both electronic logging devices and traditional paper logs share the fundamental goal of tracking a driver’s HOS, their mechanics and advantages paint a very different picture. Let’s explore the main distinctions that set these two methods apart:
- Automation vs. manual input. ELDs offer a streamlined and automated approach. These advanced devices seamlessly integrate with a vehicle’s engine, automatically logging driving hours without the need for manual data entry. This minimizes the potential for human errors associated with handwritten records. On the other hand, paper logs require drivers to manually record each driving session, encompassing start times, stops, and distances covered. While a classic approach, it can lead to inaccuracies, omitted entries, and operational inefficiencies.
- Precision and accuracy. ELDs eliminate the need for manual calculations, ensuring that driving hours are accurately and comprehensively recorded. The systematic digital tracking leaves no room for miscalculations or uncertainties, enhancing overall compliance. In contrast, paper logs are susceptible to mathematical errors and inconsistencies. Adding up hours and calculating driving intervals manually requires more time and introduces the potential for mistakes that could impact regulatory compliance.
- Handling malfunctions. In the event of an ELD malfunction, drivers are typically required to switch temporarily to paper logs to maintain compliance.
Today, ELDs represent the contemporary standard for hours of service tracking. Their automation, precision, and adaptability contribute to compliant operations.

What CMV Drivers Must Use Electronic Logbooks?
In Canada, the requirement for commercial motor vehicle CMV drivers to use electronic logbooks ELDs is based on specific criteria. The Canadian ELD mandate applies to CMV drivers who meet the following conditions:
- Interprovincial operations. CMV drivers involved in interprovincial operations, which means driving across provincial or territorial boundaries, are generally required to use ELDs. This applies to both Canadian and non-Canadian drivers operating in Canada.
- Exceeding 160 kilometers. ELDs are mandatory for CMV drivers who travel more than 160 kilometers (approximately 100 miles) from their home terminal or base of operations within a single day.
However, there are specific exemptions and exceptions outlined in the regulations. Here are some of the key groups that are exempt from using electronic logs:
- Drivers using pre-2000 vehicles. Drivers operating commercial vehicles manufactured before the year 2000 are typically exempt from the mandate. However, if the vehicle is from 2000 or later and has an engine manufactured before 2000, it may not qualify for this exemption.
- Rental vehicles. If a CMV is being rented for a period of 30 days or less and will not be used by the same driver for a longer period, ELD usage may not be required.
- Federal permit holders. Drivers working for motor carriers operating under a federal permit issued by a provincial director may be exempt from ELD requirements.
- Exemptions granted by section 16. Some drivers and carriers may be granted exemptions under section 16 of the Motor Vehicle Transport Act.
- Emergency service vehicles. Drivers operating emergency service vehicles, such as fire trucks or ambulances, may be exempt from ELD requirements.
It’s important to note that the use of ELDs in Canada is primarily regulated by the federal government, and additional specific requirements and exemptions may apply based on the jurisdiction and the nature of the CMV operation. CMV drivers and carriers should consult Transport Canada and relevant provincial or territorial authorities to ensure they fully understand the applicable ELD regulations and exemptions for their specific circumstances.
ELD Requirements For Intraprovincial CMV Drivers
While interprovincial operations in Canada involve the transportation of goods and vehicles across provincial or territorial boundaries, intraprovincial operations are focused exclusively on activities conducted within one province or territory. As electronic logging devices (ELDs) became federally mandated in Canada, some provinces and territories updated their intraprovincial regulations to include ELD requirements, ensuring consistency and compliance. Here are a few examples:
- British Columbia. British Columbia has implemented ELD requirements for intraprovincial commercial motor vehicle (CMV) drivers, aligning with federal regulations. These requirements are overseen by the British Columbia Ministry of Transportation and Infrastructure and aim to enhance road safety and ensure accurate tracking of hours of service (HOS).
- Ontario. Ontario also requires intraprovincial CMV drivers to use ELDs for recording their driving hours. These requirements are enforced by the Ontario Ministry of Transportation, contributing to improved HOS compliance and road safety.
- Quebec. Quebec has adopted ELD requirements for intraprovincial CMV drivers. The Société de l’assurance automobile du Québec (SAAQ) oversees these regulations to enhance HOS tracking and overall safety.
- Alberta. In Alberta, intraprovincial CMV drivers are subject to ELD requirements. These regulations are enforced by Alberta Transportation, aiming to ensure accurate recording of driving hours and promote safety.
- Saskatchewan. Saskatchewan is another province that has implemented ELD requirements for intraprovincial CMV drivers. The Saskatchewan Ministry of Highways and Infrastructure oversees these regulations to facilitate compliance with HOS rules and enhance road safety.
It’s crucial for intraprovincial drivers in Canada to stay informed about their province’s or territory’s specific ELD regulations and compliance requirements. Ensure that your chosen ELD provider supports these rules to avoid fines and operational disruptions.
HOS247 Is a Top-Rated ELD Provider
Choosing a reputable ELD provider like HOS247 is essential to conduct efficient and compliant operations. HOS247 offers electronic logbook devices tailored for owner-operators and fleets of all sizes. As you navigate the nuances of the ELD mandates, the support and expertise of HOS247 will help you remain confidently compliant while optimizing your trucking operations.
The HOS247 electronic logging system supports all applicable federal, provincial, and territorial HOS rules to keep truckers compliant and productive. Here’s why truckers across the nation are choosing HOS247:
- Top-rated customer support. Our customer support reps are available Monday through Sunday to help with any issues that might arise. Also, we understand that effective communication is essential. That’s why our multilingual customer support team is proficient in English, Spanish, Russian, and Polish. No matter your preferred language, we’re here to ensure your queries are met with swift and accurate resolutions.
- Driver-centric approach. We’ve revolutionized the logging experience with truckers in mind. HOS247’s user-friendly logbook app features an intuitive design that streamlines the tracking process, ultimately boosting driver satisfaction and performance.
- Quality hardware. Our reliable hardware guarantees a trouble-free installation process, reinforced by a one-year free replacement warranty.
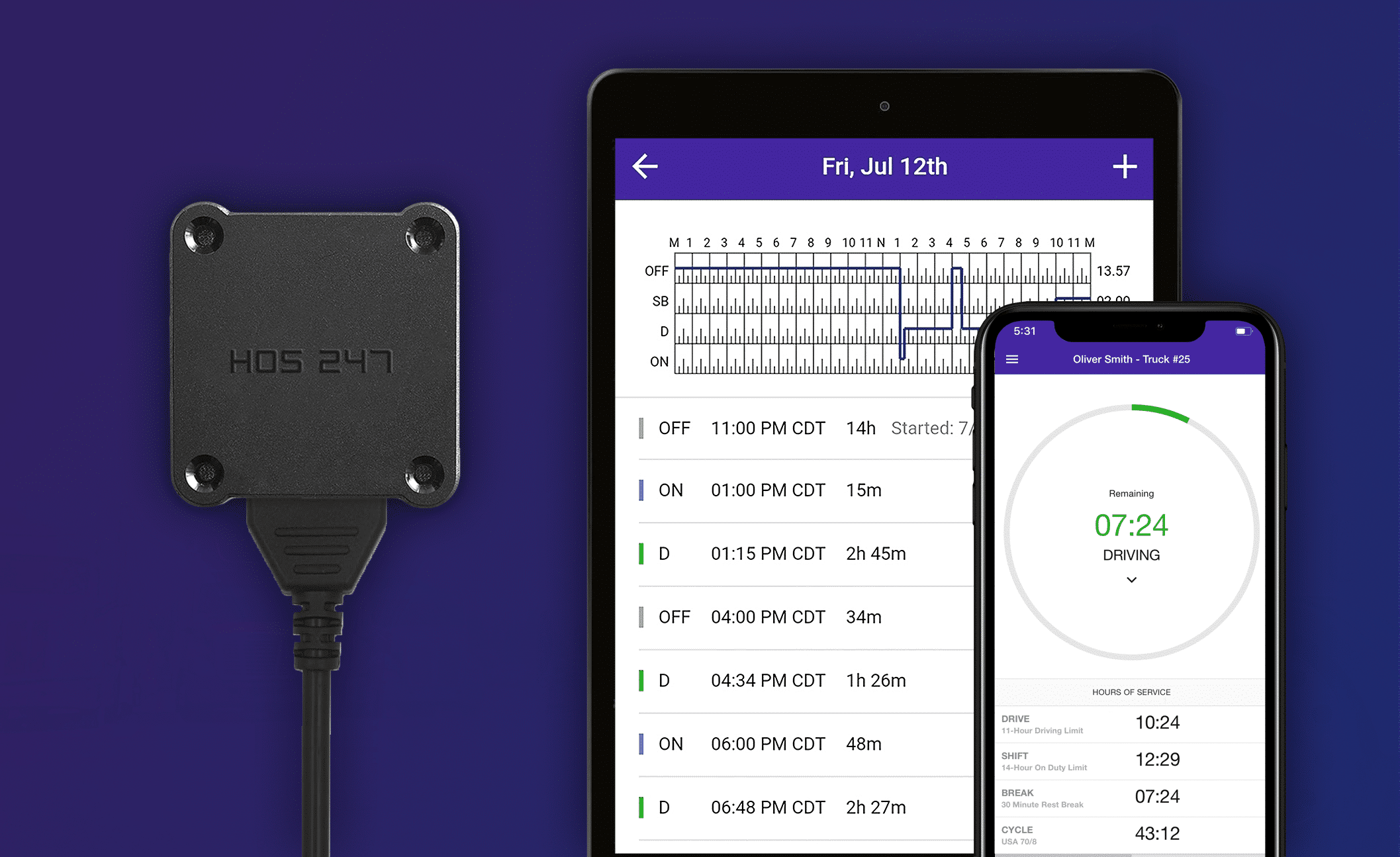
- Seamless connectivity. Stable Bluetooth connectivity ensures flawless data transfer between the hardware and app, ensuring consistent and dependable reporting.
- Operational optimization. Real-time GPS enhances fleet visibility, while driver vehicle inspection reports and fault code notifications contribute to enhanced safety and prolonged vehicle longevity.
- Flexibility. HOS247 operates under a no-contract policy, a two-week trial period with straightforward returns, and subscription plans that can be paid monthly or yearly to accommodate each carrier’s needs.
- Cost savings. Without ELD, you can steer clear of costly violations and streamline your operations, thereby reducing expenses and increasing profitability.
In an evolving trucking landscape, adopting ELDs is no longer a choice but a necessity for streamlined operations, compliance, and heightened safety. HOS247 is here to support your trucking journey with efficient and compliant ELD solutions.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











In today’s highly competitive trucking industry, fleet managers face numerous challenges in ensuring the efficiency, safety, and profitability of their operations. One of the most effective tools for addressing these challenges is GPS fleet tracking technology. By providing real-time visibility

The ELD electronic logging device will become an essential tool for trucking professionals when Transport Canada’s mandate is fully enforced. This legislation is aimed at commercial vehicle drivers who operate under HOS rules and are required to keep records of

Today, there are many options to make drivers’ daily operations more organized, efficient and safe. Among them is the electronic logging device (ELD), which is required for most commercial drivers to stay compliant with federal regulations. It automates log keeping