Installing an electronic logging device shouldn’t be complicated, but many truckers find themselves overwhelmed by confusing instructions, compatibility issues, and the fear of getting it wrong. You’re not alone if you’ve been putting off this upgrade or struggling with a current ELD that seems more trouble than it’s worth.
This guide walks you through everything you need to know about elog installation, from choosing the right device to troubleshooting common problems. Whether you’re installing your first ELD or switching from a system that’s been giving you headaches, you’ll find practical, straightforward advice that gets you compliant and back on the road quickly.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
What Every Trucker Needs to Know about Elogs
An electronic logging device (ELD), or elog, is a piece of hardware that plugs directly into your truck’s engine computer to automatically record your driving time, vehicle movement, miles driven, and engine hours. Think of it as a digital replacement for the paper logbooks you might remember – except it’s connected to your truck’s brain and can’t be “adjusted” like the old paper logs.
How ELDs Work: Hardware + App
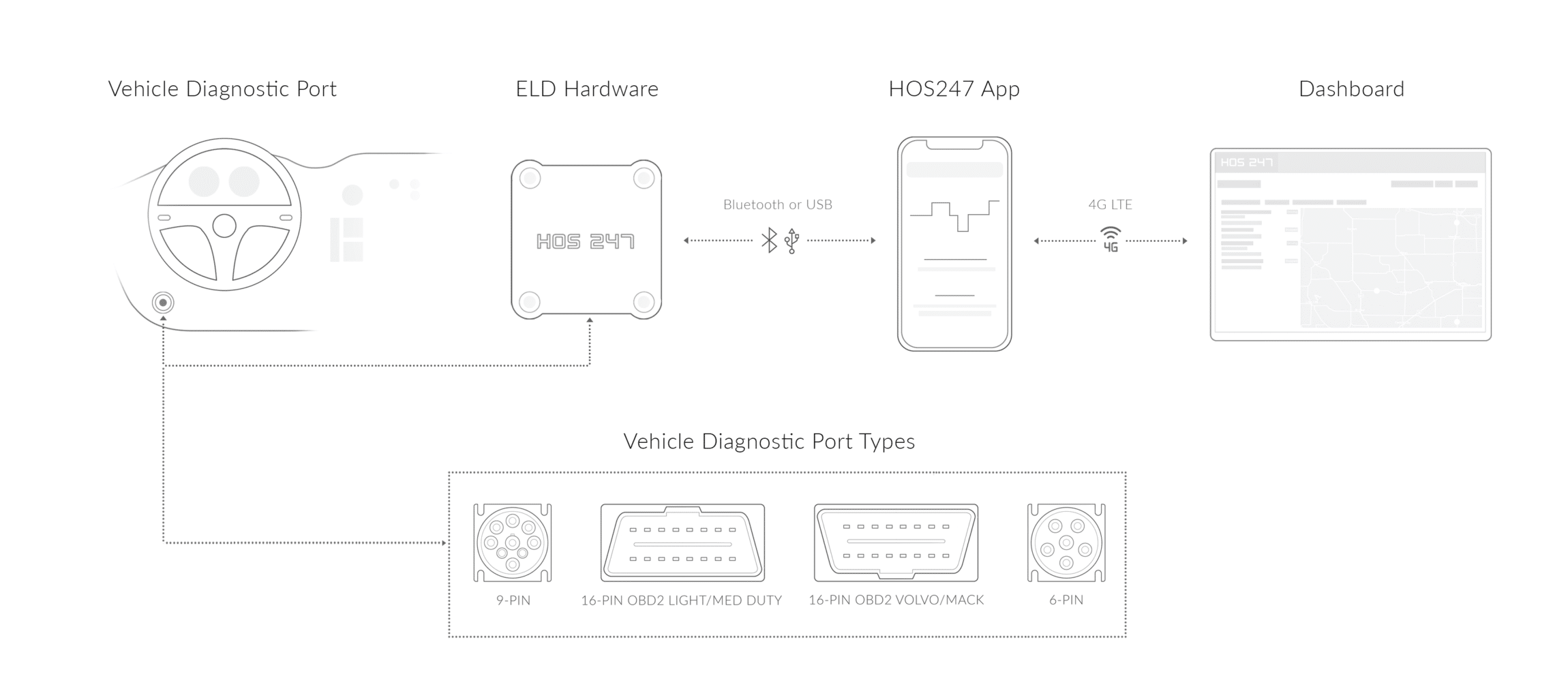
The device consists of two main parts: a small electronic unit that plugs into your truck’s diagnostic port (usually about the size of a smartphone), and a mobile app that runs on your tablet or smartphone. The hardware captures data from your engine computer, while the app displays your hours of service information and lets you change your duty status when needed.
ELDs vs. AOBRDs and Paper Logs
ELDs are different from the older Automatic Onboard Recording Devices (AOBRDs) that some fleets used before the mandate. While AOBRDs could estimate driving time, ELDs are directly connected to the engine and provide more accurate, tamper-proof records. Paper logs, meanwhile, are only allowed as backup when your electronic logbook malfunctions – you can’t legally run paper logs as your primary logging method if your truck is subject to the mandate.
Who Needs an ELD (and Who Doesn’t)
The FMCSA requires elogs for most commercial drivers who are currently required to maintain hours of service records. This includes most long-haul truckers, but there are some exceptions. You don’t need an ELD if you operate within a 150 air-mile radius of your work location, drive a truck manufactured before model year 2000, are delivering the truck you are driving, or use paper logs for 8 or less days within 30 days).
FMCSA Compliance
All approved ELDs must meet strict technical specifications set by the FMCSA, including tamper-resistant features, standardized data transfer capabilities for roadside inspections, and automatic malfunction detection.

Pre-Elogs Installation Preparation
Getting your elog installation right starts long before you touch any cables or download apps. Taking time to choose the right device and gather everything you need upfront will save you hours of frustration later.
Choosing the Right ELD
Not all ELDs offer the same quality of service, and the cheapest option often costs you more in the long run through poor support, unreliable hardware, or hidden fees. Start by verifying that any ELD you’re considering appears on the FMCSA’s registered device list – using a non-certified device is the same as not having an ELD at all in the eyes of DOT officers.
When evaluating ELD options, look for these essential features:
- Regulatory compliance. Verify the device appears on the official FMCSA registered ELD list and meets all current federal requirements for electronic logging.
- Truck compatibility. Ensure the system works with your specific make, model, and year of truck without requiring expensive adapters or modifications.
- Intuitive design. The interface should be easy to navigate while driving, with clear displays and simple controls that don’t create safety hazards.
- Reliable customer service. Look for providers with responsive support teams that understand trucking operations and can help resolve issues quickly.
- Clear pricing structure. Avoid companies with hidden fees, complex contracts, or surprise charges that aren’t disclosed upfront.
- Proven hardware durability. Choose devices with solid construction, good warranties, and positive reviews from actual drivers who’ve used them long-term.
- Simple elog installation process. The best systems offer straightforward setup that drivers can complete themselves without technical expertise or service calls.
- Regular software updates. Systems should automatically stay current with changing regulations and receive bug fixes without additional costs.
- Driver-friendly features. Look for user-friendly apps and easy log management capabilities that make compliance easier.
Reading real driver reviews, not just marketing materials, gives you insight into day-to-day usability and long-term reliability. Pay attention to complaints about frequent malfunctions, poor customer service experiences, or unexpected fees that might not be obvious during initial research.
Tools and Materials Needed
Elogs installation is designed to be simple, but having everything ready beforehand prevents delays and ensures a smooth process. Most installations require minimal tools, though having a few basics on hand helps with cable management and device mounting.
Elog Software
Your smartphone or tablet is the most critical component after the ELD hardware itself. Check the ELD manufacturer’s app requirements carefully – some older devices may not support the latest apps, and insufficient memory or processing power can cause performance issues. Android devices typically need version 7.0 or newer, while iOS devices should run iOS 12 or later. Ensure your device has adequate storage space for the app and log data.
Internet connectivity during setup is essential for account activation and initial configuration. While the logbook will work without constant internet once installed, you’ll need a reliable connection during the initial setup process. If you’re installing at a truck stop or other location with poor cell service, consider waiting until you’re somewhere with better connectivity.
Elog Hardware
Most systems come with all necessary cables, but verify this before starting your installation. Some providers include multiple cable types to ensure compatibility with different diagnostic port configurations. Keep your user manual and installation guide handy – even with simple installations, referring to manufacturer-specific instructions prevents mistakes that could damage your truck’s electrical system.
How to Install Elog Systems — Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Modern ELD installation is designed for drivers to handle themselves, eliminating expensive service calls and getting you compliant faster. Follow these steps carefully, and you’ll have your system running in under 30 minutes.
Finding the Diagnostic Port
The diagnostic port is your gateway to the truck’s computer system, and locating it is usually the most challenging part of installation. In most trucks, you’ll find it within three feet of the driver’s seat, though the exact location varies by manufacturer and model year.
Common Locations and Connector Types
Start by looking under the dashboard on the driver’s side. The port often sits behind small plastic covers or tucked up under the dash where it’s protected from road debris and accidental damage. Some trucks have the port mounted on the lower dash panel, while others place it on the steering column or near the driver’s left knee.
Different truck types use different connector styles
- Heavy-duty trucks typically use either 6-pin or 9-pin round connectors that look like thick electrical plugs. These J1939 ports are usually green or black and clearly labeled.
- Light and medium-duty vehicles, along with newer Volvo and Mack trucks, often use the standard OBD-II rectangular port that’s common in passenger cars.
Troubleshooting Port Location
If you can’t locate the port after checking obvious locations, consult your truck’s manual or call the manufacturer’s service line. Some older trucks have ports in unusual locations like behind the sleeper or under passenger-side panels. Don’t force connectors that don’t fit easily – you should never need significant pressure to connect an ELD cable.
Physical Installation
Once you’ve located the diagnostic port, installation becomes straightforward. Most devices follow a simple plug-and-play design that requires no tools or permanent modifications to your truck.
Connecting the ELD Cable
Connect the ELD cable to the diagnostic port first, ensuring it clicks or locks securely in place. A loose connection will cause intermittent data problems that are frustrating to diagnose later. The connection should feel solid without excessive force – if you’re fighting to get the connector seated, double-check that you have the right cable type.
Mounting the ELD Device
Mount the elog device itself in a location where it’s protected from damage but accessible if needed. Many drivers prefer spots on the dashboard where the device is visible but not obstructing important controls or gauges. Some units include mounting brackets or adhesive strips, while others are designed to sit loose in a secure location.
Cable Routing and Safety
Route cables neatly to prevent damage and avoid interfering with vehicle operation. Avoid running cables across pedals, steering components, or anywhere they might get pinched by moving parts. Simple cable ties or clips keep wiring organized and professional-looking.
Software Setup: Fleet Manager Portal and Elog App
1. Downloading the ELD App
Download the ELD app from your device’s official Android or iOS app store before starting the software setup process. Avoid third-party app sources that might contain outdated or modified versions. Create your user account according to the manufacturer’s instructions, which typically requires basic information like your name, CDL number, and company details.
2. Setting Up Credentials in the Management Portal
Before drivers can use the mobile app, credentials must be set up through the web-based management portal. Even owner-operators need both manager and driver accounts since FMCSA regulations require separate credentials for administrative functions versus daily logging. The fleet manager portal allows you to add drivers, assign vehicles, configure Hours of Service rules, and manage company settings. Owner-operators use this same portal to manage their own operations, but they’ll log in with different credentials than they use for daily driving.
3. Account Creation and Access
Your ELD provider can guide you through creating both accounts during the signup process. If you’re joining an existing fleet, your fleet manager will create your driver profile and provide your login credentials. Make sure you receive both your driver app login information and access to the management portal if you need administrative control.
4. Pairing Your Device with ELD Hardware
Bluetooth pairing connects your smartphone or tablet to the hardware. Enable Bluetooth on your mobile device, then follow the app’s pairing instructions. Most systems automatically detect nearby ELD devices, but you may need to select your specific unit from a list. Some systems also support USB connections if Bluetooth proves problematic.
5. Initial Configuration and Profile Verification
Initial configuration includes verifying your driver profile information, selecting appropriate Hours of Service rules, and confirming any company-specific settings. Take time to ensure that your information matches exactly what was entered in the management portal – mismatched data can cause compliance problems during inspections.
6. System Testing and Feature Validation
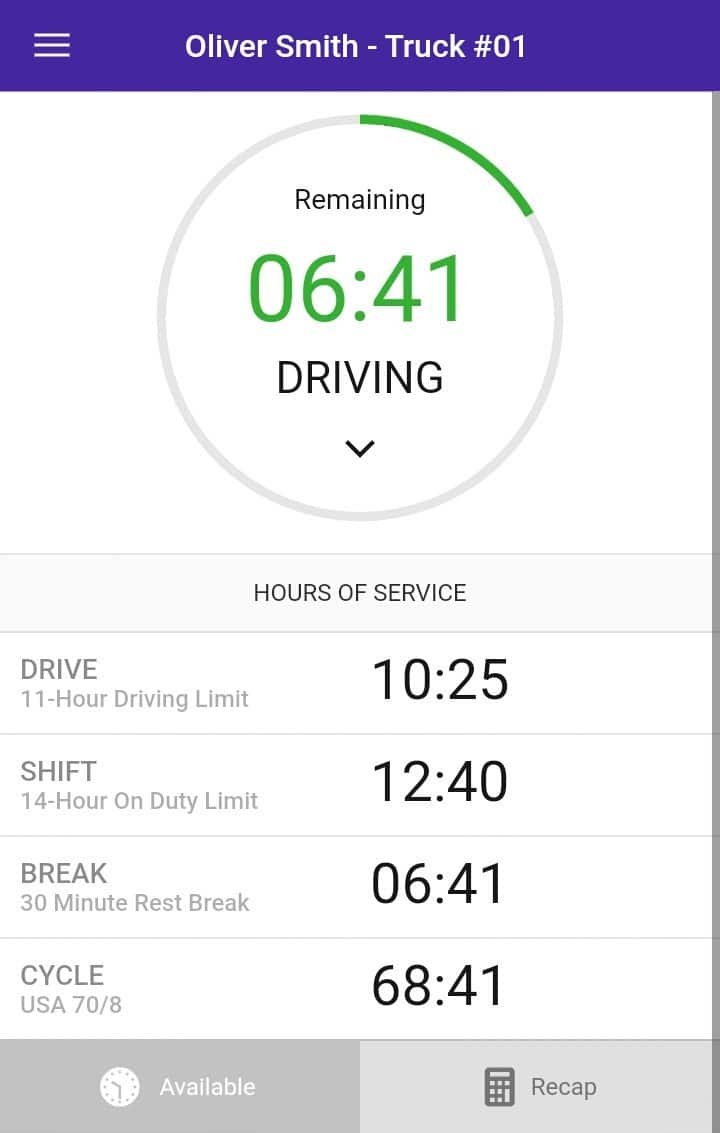
Test the system by changing duty status and confirming that the app responds appropriately. Verify that your hours of service calculations appear correct and that any fleet-specific features like messaging or dispatch integration are working properly.
7. Final Verification and Compliance Check
The final step involves verifying that the ELD is recording data correctly. Start your truck and drive slowly around the parking lot while monitoring the app. You should see driving time begin accumulating and your duty status automatically change to “Driving” once you exceed 5 mph. If data isn’t appearing or seems incorrect, review your connections and consult the troubleshooting guide before concluding installation.
HOS247 Electronic Logbook Benefits
When choosing an ELD system, HOS247 stands out for its driver-first approach and commitment to making compliance simple rather than complicated. Our system is designed by people who understand that truckers need technology that works reliably without creating new headaches.
We offer several key advantages that make it a top choice for drivers switching from other elog systems or installing their first device:
- Driver-friendly interface. The user interface prioritizes clarity and speed over flashy features, requiring just two taps to change status and keeping critical information visible without screen clutter.
- True plug-and-play installation. The system automatically detects your truck’s diagnostic port type and configures itself accordingly, with most drivers completing setup in under 20 minutes without technical knowledge.
- Knowledgeable customer support. Support representatives understand trucking operations and provide practical solutions rather than generic troubleshooting scripts, with a callback policy that ensures you’re never left stranded.
- Automated maintenance alerts. The system tracks vehicle diagnostics and notifies you of potential issues before they become expensive roadside emergencies, helping prevent breakdowns.
- Real-time data synchronization. Your logs stay current and accessible whether you’re at a DOT inspection or managing your business from home, eliminating data loss concerns.
- Risk-free 14-day trial. Test the complete system with full feature access and no credit card required, allowing thorough evaluation before commitment.
- Transparent pricing structure. One clear monthly rate includes hardware, software, and support with no activation fees, hidden charges, or mandatory long-term contracts.
- Multilingual support available. Customer service is available in English, Spanish, Russian, and Polish to serve drivers who prefer support in their native language.
The system maintains FMCSA compliance automatically through regular software updates, so you never worry about whether your ELD meets current regulations or face violations due to outdated software. HOS247 handles compliance requirements so you can focus on driving and growing your business.

Common Elog Installation Problems and Troubleshooting
Even with straightforward ELD systems, installation doesn’t always go perfectly the first time. Understanding common problems and their solutions helps you resolve issues quickly without expensive service calls or compliance delays.
Connection Issues
Bluetooth Pairing Problems
Bluetooth pairing failures are the most common installation issue. Start with basic verification: ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your device and test it with another device to confirm it’s working. Stay within three feet of the ardware device during pairing and make sure no other Bluetooth devices are trying to connect simultaneously.
If basic checks don’t resolve the issue:
- Clear Bluetooth cache on Android: Settings > Apps > Bluetooth > Storage > Clear Cache.
- On iOS: Forget all paired devices, restart the phone, then attempt ELD pairing.
- Check for physical pairing buttons on the ELD unit that must be pressed during connection.
- Verify you’re connecting to the correct ELD by checking serial numbers if multiple devices are nearby.
Diagnostic Port Connection Problems
Connection issues usually result from loose cables or using incorrect port types. Remove and reconnect the cable, ensuring it seats completely with a definite click or resistance. Inspect the cable for physical damage like bent pins or cracked housings that prevent proper connection.
Additional diagnostic port troubleshooting:
- Verify you’re using the correct diagnostic port according to your ELD manufacturer’s specifications.
- Check that the port isn’t damaged, corroded, or obstructed.
- Start your truck and let it run for several minutes, as some trucks require engine power for adequate diagnostic port voltage.
Power-Related Malfunctions
Some devices need the engine running to receive sufficient power from the diagnostic port. If your ELD appears to connect but doesn’t maintain stable operation, try keeping the engine running during initial setup and testing.
Software Problems
App Synchronization Failures
Synchronization problems typically stem from connectivity issues or app glitches. First, verify your cellular or WiFi connection is working properly, as ELD apps require internet access for setup and periodic data uploads.
If connectivity isn’t the issue:
- Force-close the elog app completely and restart it.
- Android users: Use the recent apps button to swipe away the app, then reopen.
- iOS users: Double-tap home button and swipe up on the app to close, then restart.
Data Transfer and GPS Issues
DOT inspection data transfer problems can create compliance violations. Practice using all available transfer methods (email, USB, Bluetooth) before you need them during an actual inspection. Keep backup methods ready in case your primary option fails.
GPS signal problems affect required location data accuracy. Enable location services for the ELD app in your device settings. Some trucks have windshields or components that interfere with GPS signals, potentially requiring external GPS antennas for reliable reception.

When to Call Support
Recognize when problems exceed simple troubleshooting and require professional assistance. Contact support immediately if you see error messages indicating ECM communication failures, as these might indicate serious electrical problems that could damage your truck’s computer systems.
Persistent data recording failures that prevent the ELD from capturing driving time require immediate attention to avoid compliance violations. Don’t continue operating if your ELD isn’t recording hours properly – use paper logs as backup and contact support for emergency assistance.
Preparing for a Support Call
Document error messages, device serial numbers, and the exact steps that led to problems before calling support. This information helps support representatives diagnose issues more quickly and provide targeted solutions. Take screenshots of error screens when possible, as visual information often clarifies problems that are difficult to describe over the phone.
Keep your truck’s make, model, year, and engine type readily available when contacting support, as this information affects troubleshooting procedures and compatibility requirements. Having your account information and driver credentials available also speeds up the support process.

Post-Elog Installation Best Practices
Getting your ELD installed correctly is just the beginning. Taking time to properly test and maintain your system prevents compliance problems and ensures reliable operation when you need it most.
Testing Your ELD Thoroughly
Don’t assume your electronic logbook is working correctly just because it powers on and connects to your phone. Spend at least 30 minutes testing all functions before hitting the road. Drive around the parking lot while monitoring the app to verify that driving time accumulates automatically and your duty status switches to “Driving” when you exceed 5 mph.
Test duty status changes by switching between On Duty, Off Duty, and Sleeper Berth modes. Each change should register immediately in the app with the correct timestamp and location. Practice changing status while stationary, as you’ll need to do this quickly during actual operations.
Verify that your Hours of Service calculations appear accurate and match your expectations based on current regulations. Check that violation warnings activate appropriately when you approach daily or weekly limits. Test the DOT inspection mode by practicing data transfers via email, USB, or Bluetooth to ensure you can provide logs during roadside inspections.
Training on Proper Usage
Even user-friendly systems require some learning to use efficiently. Familiarize yourself with the elog app’s layout and menu structure so you can navigate quickly without taking attention away from driving. Learn the difference between automated status changes and manual edits, understanding when each is appropriate.
Practice adding notes to duty status changes, as these annotations help during inspections and provide context for unusual entries. Understand your ELD’s malfunction indicators and what actions to take if error messages appear while driving.
Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Check your ELD connections weekly to ensure cables remain secure and aren’t showing signs of wear. Inspect mounting locations to verify the device hasn’t shifted or become loose due to road vibrations.
Keep your logbook app updated by enabling automatic updates in your device’s app store settings. Monitor your data usage if you’re on a limited cellular plan, as apps periodically upload log data to comply with regulations.
Backup Documentation Procedures
Despite ELD reliability, malfunctions can occur without warning. Keep paper log forms in your truck and understand how to complete them manually if your system fails. Know the specific steps required to document any malfunctions according to FMCSA regulations.
Maintain records of your device’s serial number, manufacturer information, and support contact details in case you need assistance while away from home base. Some drivers keep photos of their ELD setup on their phones to help troubleshoot connection problems or assist support representatives.
Cost Considerations
Ask potential providers how to install elog hardware before you make a purchase. Some companies let you handle the work yourself while others require professional installation services. Understanding these expenses helps you budget appropriately and avoid unexpected charges.
Self-Installation vs Professional Services
Most modern ELD systems are designed for driver self-installation, eliminating service fees that typically range from $50 to $200 per truck. Professional installation makes sense if you’re uncomfortable with technology, have an older truck with complex wiring, or need multiple trucks equipped simultaneously.
Self-installation saves money and gives you a better understanding of your system, making future troubleshooting easier. However, professional installation may include warranty coverage for the installation work itself, protecting you if connection problems develop later.
Hidden Costs to Watch For
Many ELD providers advertise low monthly rates but add charges that significantly increase your actual costs. Activation fees, equipment deposits, and mandatory accessories can add $100 or more to your first bill. Some companies charge extra for customer support, software updates, or data transfer capabilities that should be included in basic service.
Contract cancellation fees can cost hundreds of dollars if you need to switch providers due to poor service or equipment problems. Read the fine print carefully and ask specific questions about all potential charges before signing up.
Data overage charges affect drivers with limited cellular plans. While elog data usage is typically minimal, some systems upload more data than others. Unlimited data plans eliminate this concern but may cost more than limited plans initially.
Return on Investment
Quality logging systems often pay for themselves through improved efficiency and violation prevention. Automated hours tracking helps you maximize available driving time within legal limits, potentially increasing your earning capacity.
Avoiding just one HOS violation can save you hundreds or even thousands in fines, easily covering a year’s worth of ELD service costs. Beyond compliance, advanced features like real-time route data and preventive maintenance alerts can lower fuel consumption and reduce the risk of expensive roadside breakdowns. For drivers and carriers, the right ELD is not just a regulatory requirement but also a smart business investment.
Comparing Major Providers
ELD pricing varies widely among providers, but the cheapest option often costs more in the long run through poor reliability, limited support, or hidden fees. Focus on total cost of ownership including hardware, monthly service, support quality, and contract flexibility rather than just the advertised monthly rate.
Consider trial periods and money-back guarantees when comparing providers. Companies confident in their service quality offer meaningful trial periods that let you test real-world performance before committing to long-term contracts.

Conclusion
Installing an ELD doesn’t have to be complicated or stressful when you choose the right system and follow proper procedures. The key is selecting hardware that matches your truck’s requirements and software designed with drivers in mind rather than fleet managers or accountants.
Remember that FMCSA compliance is non-negotiable, but achieving compliance shouldn’t make your job harder or more expensive than necessary. Quality electronic logbook providers offer straightforward installation, reliable operation, and support when you need it most.
Don’t let ELD compliance concerns keep you off the road or force you to accept substandard service from providers who don’t understand trucking operations. Take advantage of HOS247’s trial offer to experience how elog technology should work – reliably, simply, and without surprises. Your compliance and peace of mind are worth the few minutes it takes to explore better electronic logbook options.

As an expert in B2B and B2C sales, I’ve dedicated myself to perfecting sales processes and client retention strategies in the logistics and trucking industry. I have significantly contributed to the expansion of the ELD service, catering to retail and wholesale clients in need of HOS247 ELD solutions. My unwavering commitment to implementing state-of-the-art sales techniques and technologies ensures the continuous growth and success of businesses I work with.











An electronic logging device is a federally mandated device for most commercial driver license holders who must maintain records of duty status. These devices help monitor the drivers’ time on the road to meet hours of service compliance. HOS247 is

A quick search for a “drivers logbook app Android” in app distribution platforms will return hundreds of results. From free basic trackers to paid subscription services, the options seem endless. For professional truck drivers and fleet managers, one critical question

All applicable hotshot drivers and carriers must comply with the ELD mandate. Drivers should be aware of their responsibility to keep Records of Duty Status (RODS), electronic logs, and maintain their electronic logging devices (ELD). For more information on DOT