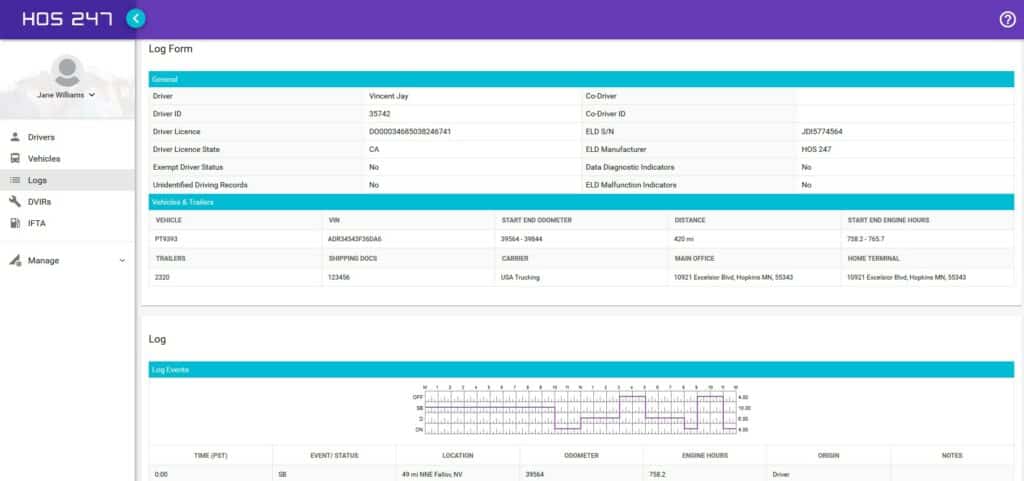
Benefits of HOS247 Electronic Logs
Besides helping drivers and carriers meet e-log compliance, HOS247 is a top-rated DOT electronic logbook provider highly trusted by fleets and owner-operators alike. The benefits of trusting HOS247 to help maintain electronic logs are many and include:
- Hardware that is easy to use and easy to install. The device is installed within minutes. It connects to drivers’ smartphones and tablets using Bluetooth and has been designed with the highest quality to provide a stable connection.
- The all-in-one plan option offers tablets for drivers who don’t already have them, including data.
- Simple setup and usage. Optional driver onboarding training is available over the phone.
- A reliable, multilingual support team is available to help drivers answer compliance issues on the road.
- No-contract policy to allow customers to change or customize plans at any time to meet the changing needs of their fleets.
- Two-week trial: if you are not satisfied, you can return the product within the first two weeks for a full refund, no questions asked.
- Ability to manage electronic driver-vehicle inspection reports (DVIRs) in a few clicks to ensure compliance and safety.
- Protection from the cost of expensive violations: HOS247 electronic logs help drivers pass DOT inspections.
- An intuitive fleet manager portal that increases fleet visibility and boosts productivity.
What Is the Canadian ELD Mandate?
The Canadian government first published the Canadian ELD mandate order in December 2017. On June 13, 2019, Marc Garneau, Canadian Minister of Transport, officially announced that it was set to go into full operation on June 12, 2021. However, Canadian authorities decided to establish a one-year period of progressive enforcement without penalties so that full compliance was expected by June 12, 2022, but this period was extended by six months. The new full enforcement date has been set to January 1, 2023. As of that date, all carriers must switch from paper logs to automatic electronic mileage log devices.
Instead of using manual paper logs, the new regulation will require commercial vehicles to capture service hours automatically using an electronic logging device. The ELD mandate’s objective is to create a safer environment for drivers where they can easily track and manage records of duty status (RODS). According to the Canada Gazette, the new legislation’s benefits are worth over $380 million, with a $55 million annualized value, due to the avoidance of thousands of annual crashes through reduced driver fatigue and a vast decrease in the amount of paperwork required.
There are several similarities between the Canadian ELD mandate and the existing U.S. mandate. There is an opportunity to promote economic growth by harmonizing the two regulations. However, a fundamental difference is the Canadian mandate requires ELDs to be certified by a third-party rather than self-certified, which is permitted in the U.S. Drivers in Canada also don’t need to transfer logs to a federal system such as eRODS.
What Is an ELD?
According to Transport Canada, a certified mandatory device or technology that can automatically log driving time and records of duty status is an acceptable ELD. There are significant benefits of ELDs for the driving sector. The devices enable quicker enforcement checks, less paperwork, and minimize the potential for driver fatigue. Arguably, one of the most crucial features is that the mandate offers excellent economic value by implementing ELDs to harmonize with U.S. standards.
Semi truck electronic logs can be installed within minutes by plugging them in, logging on using a device such as a smartphone or a tablet, and then connecting through Bluetooth. As soon as a vehicle moves at more than 8 km/h, the ELD status switches to Driving, and it will begin to capture times automatically.
Once the driving data is recorded, it can be accessed remotely by compliance managers or dispatchers, for example. It can also be viewed by the driver or a Transport Canada officer during a roadside inspection. Any smartphone or wireless device that meets the mandate’s technical guidelines and connects to an engine computer module of a vehicle can be used.
ELDs do not collect data about vehicle performance such as speed, steering, or braking, but only information relating to driver compliance with hours of service regulations.
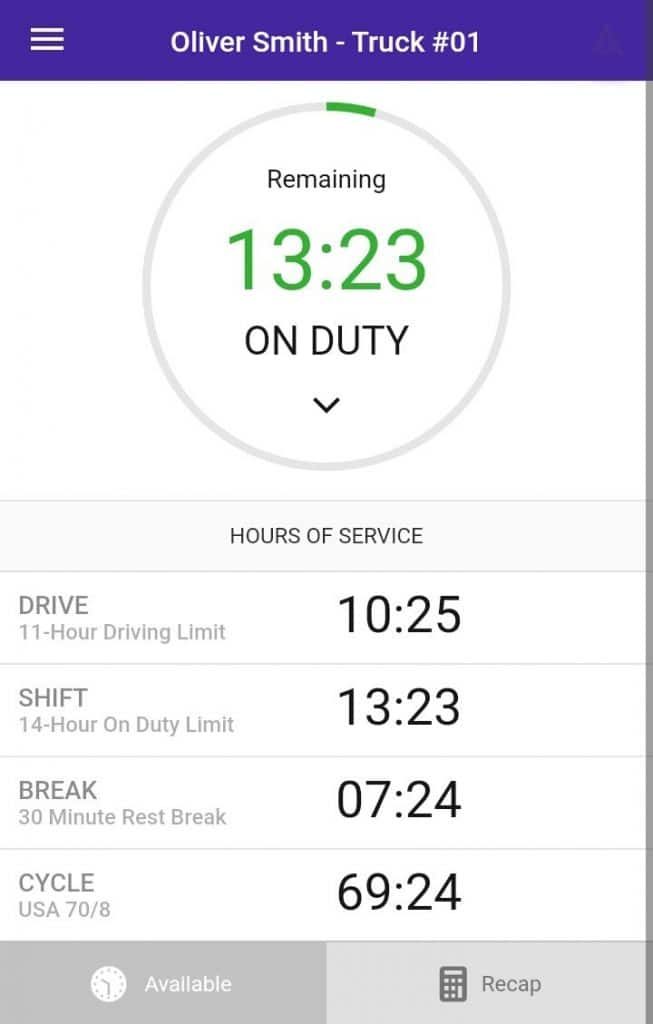
Canada ELD Mandate Exemptions
There are some notable exemptions to the Canadian ELD Mandate regarding electronic logs for older trucks. First, the regulations do not apply to vehicles with an engine model built before the year 2000. If you have a vehicle registration model newer than 2000 but without an engine control module (ECM), the motor carrier needs to find an ELD that does not depend on ECM connectivity.
Drivers do not need to keep a logbook when they operate within a 160km radius of their home terminal and are therefore exempt from the ELD mandate requirements. Short-term rentals of less than thirty days and commercial vehicles that operate under a specific permit or have a statutory exemption also do not need to comply.
Furthermore, in cases where an electronic logbook malfunctions, the driver has fourteen days in which they can maintain paper logs, at the end of which the device must be returned to full functionality. If they return to a home terminal before the end of the fourteen days, the ELD should be repaired at that point. In the U.S. Mandate, drivers are permitted eight days to resolve the problem.
Canadian ELD FAQ
Motor carriers are responsible for using third-party certified ELDs in Canada. Third-party certification of ELDs is a requirement from Transport Canada, which will be engaging with suitable entities to manage the role.
A device that complies with the US is not necessarily compliant with Canadian rules. The regulations are similar to ensure interoperability, but the Canadian ELD Mandate includes additional terms around existing HOS regulations.
An ELD automatically logs data elements at certain time intervals. Location, date, time, engine hours, distance, and identification information for the driver, vehicle, motor carrier, and the authenticated user are all recorded.
There are several points that an ELD will record location information. When the driver powers on or shuts off the engine, there is a change of operating jurisdiction or duty status, and the location will be recorded. The location data must be registered at 60-minute intervals with an ELD when the vehicle is in motion.
An electronic logging device cannot identify a street address from the location information. Instead, the latitude/longitude coordinates will convert to geolocation that approximates direction and distance to a particular location, such as a city, town, or municipality.
An electronic logging device has to automatically go into a driving status when the vehicle moves faster than eight kilometers per hour. It will stop recording once the vehicle has been at 0 km/h (stopped moving) for at least three seconds. Commercial motor vehicles must not have an in-motion state configured to anything over 8 km/h.
ELD’s will automatically record the moving time of commercial motor vehicles (CMV’s). The records are immutable, meaning that they cannot be edited.
Smartphones and other portable devices are suitable ELDs as long as they are mounted in a fixed position, visible when the driver is seated normally in the vehicle, and make part of an e-log system that is connected to the engine. All devices that meet the technical specifications of an ELD can be used.
The electronic logging device reports all information from the past 24 hours and the previous 14 days (consecutively). An official can request to view the ELD display or printout at a roadside inspection to verify compliance with the Canadian HOS Regulations. The officer may ask for documents to be electronically transferred for examination as an additional request.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











The main requirement for any electronic logging device is compliance with Transport Canada’s ELD mandate. However, there are many other factors that turn out to be crucial when looking for a reliable provider. In this article, we discuss some red

It’s a scenario every trucker in Canada dreads: you’re pulled in for a roadside inspection, the officer asks to see your logs, and your ELD won’t connect. You’re staring at a spinning wheel on your screen, trying to explain that

What Is the Best Digital Logbook for Canada HOS Compliance? Drivers have an extremely important job and are highly valuable for carrier companies. They deserve to have the best logbook available to make their work straightforward and manageable. HOS247 is