In the world of commercial trucking, staying on top of regulations is key to smooth operations. The electronic logging device (ELD) mandate, enforced by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), has reshaped how drivers and carriers track hours of service. Whether you’re a veteran of the road or just starting out, understanding these requirements is crucial. This guide breaks down the ELD mandate, offering clear insights and practical tips to ensure you’re fully compliant.
Checklist of DOT Log Book Rules and Regulations
Overall, the ELD mandate is a list of new DOT log book regulations issued by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), requiring most drivers to electronically record their hours of service instead of using a traditional paper driver log book. The DOT enforces the requirements set forth by the mandate and non-compliance can lead to fines and penalties for both drivers and carriers.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
These requirements are designed to promote road safety, prevent fatigue-related accidents, and uphold fair competition within the industry. Below is a comprehensive list of mandatory ELD requirements that all motor carriers and drivers must meet to remain compliant with federal regulations.
- The provider must be listed on the Federal FMCSA’s registered ELDs list.
- Portable ELD devices are required to be mounted in a fixed position and must be visible to the driver while seated in the normal driving position.
- An ELD information packet, either in hard copy or digital format, is required to be kept in the vehicle. This packet must include:
- A user manual detailing essential information on operating the system.
- Step-by-step instruction sheets for transferring data from the ELD to safety officials during an inspection, as well as for reporting and recordkeeping procedures during a malfunction.
- At least eight days’ worth of blank Records of Duty Status (RODS) graph grids.
- The ELD must power on and be fully functional within 1 minute of starting the vehicle and remain on until the engine is shut off.
- The log book must convert Universal Coordinated Time (UTC) to the local time standard at the driver’s home terminal, taking into account daylight saving time.
- The ELD must automatically determine the vehicle’s position in standard coordinates as an accurate geo-location.
- The log book must allow the driver to manually enter the vehicle’s location in text form when prompted.
- The system must enable motor carriers to configure each driver’s profile to claim exemptions from ELD use and to prevent unidentified driver data diagnostics errors.
- For records of unidentified drivers, the ELD must prompt the driver with a warning indicator.
- The log book must prohibit the automatic shortening of recorded driving time and ensure that the username associated with a record cannot be edited or reassigned, except under rare circumstances.
- The device must record every instance of a driver certifying or recertifying their records within a 24-hour period and associate the records with the driver, vehicle, motor carrier, and shipping document number.
- The device must be capable of determining when the vehicle is in motion and automatically set the duty status to driving; the vehicle must be at 0 mph to be considered stationary.
- The ability to print or digitally display log book data for roadside inspections must be supported by the ELD.
Remember, these regulations are not only legal requirements but also crucial measures designed to protect drivers, passengers, and the public on our roads. Always stay informed of any changes or updates to DOT regulations to ensure your compliance is continuous and your driving practices reflect the commitment to safety that is at the heart of these rules.
Who Needs Elogs?
DOT log book requirements apply to the majority of CMV drivers operating in the United States, even if they are domiciled in Canada or Mexico. Here are the key groups that must comply with the ELD mandate:
- Commercial truck drivers. Most drivers who are required to maintain records of duty status (RODS) must use an ELD. This includes drivers of vehicles with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) or gross combination weight rating (GCWR) of more than 10,000 pounds that are used for business purposes.
- Interstate commercial drivers. Drivers who operate across state lines and fall under the jurisdiction of the FMCSA must comply with the ELD mandate. This includes both property-carrying and passenger-carrying drivers.
- Drivers who maintain RODS. Drivers who are required to keep RODS for more than 8 days in a 30-day rolling period must use an ELD. This applies regardless of whether these days are consecutive.
- CDL holders operating commercial vehicles. Commercial Driver’s License (CDL) holders who operate commercial vehicles must use ELDs if they are required to keep RODS. This includes trucks and buses.
DOT Log Book Exemptions
The DOT has outlined specific exemptions to the ELD rule designed to accommodate certain types of drivers and operations where the strict application of the rule may not be necessary or practical. These exemptions are:
- Driveaway-towaway operations. If the vehicle being driven is part of the shipment , the driver is exempt from the rule.
- Pre-2000 vehicles. Vehicles with engines manufactured before the year 2000 are exempt, based on the difficulty of connecting these devices to older engines.
- Intermittent use. Drivers who are required to keep RODS not more than 8 days within a 30-day rolling period do not need to use an ELD. This can apply to drivers who do not typically travel outside of the short-haul exemption parameters but occasionally do.
- Agricultural exemptions. Certain drivers transporting agricultural commodities within a specific distance (150 air-miles) from the source of the commodities during planting and harvesting seasons are exempt from the elog requirements.
- ELD malfunction. In the event of an ELD malfunction, drivers are required to note the malfunction and can use paper logs for up to 8 days or until the device is repaired, whichever comes first.
- Short-haul exemption. DOT log book rules for local drivers accommodate those who operate within a more confined geographic area and have different requirements compared to long-haul drivers. Drivers who use the short-haul exemption must operate within a 150 air-mile radius, return to the work reporting location within 12 hours, and not drive more than 11 hours. They must also have at least 10 consecutive hours off between shifts. These drivers are not required to keep Records of Duty Status (RODS) or use elogs.
It’s important to note that while these exemptions provide relief from the ELD mandate for certain drivers and scenarios, drivers and carriers must still comply with all applicable HOS rules. Regulations and exemptions may also be updated or revised, so it’s advisable for drivers to stay informed about the latest FMCSA guidelines and requirements.
HOS247 Promotes Successful Trucking Operations
After understanding the intricacies of the ELD mandate, it’s clear that selecting the right ELD provider is crucial for compliance and operational efficiency. HOS247 stands out as a leading technology provider in ELD and fleet management solutions, designed to ease the compliance process and enhance the operational capabilities of your trucking business.
Beyond staying compliant with both current and new DOT log book rules, running the fleet efficiently and eliminating redundant administrative tasks is ideal. That’s why it’s important to trust an ELD that is not only compliant and easy to use but also has other features that simplify operations.
Electronic Log Book
- User-centric interface. The platform offers a user-friendly interface for both drivers and fleet managers, enhancing operational workflow.
- Reliable connectivity. Prioritizing consistent data transmission, HOS247 minimizes disruptions crucial for compliance and operational accuracy.
- Multilingual support. With support available seven days a week and in multiple languages, including Russian and Spanish, HOS247 ensures accessibility and assistance whenever needed.
- Integration capabilities. Seamless integration with various fleet management systems positions HOS247 as a comprehensive solution for modern fleet operations.
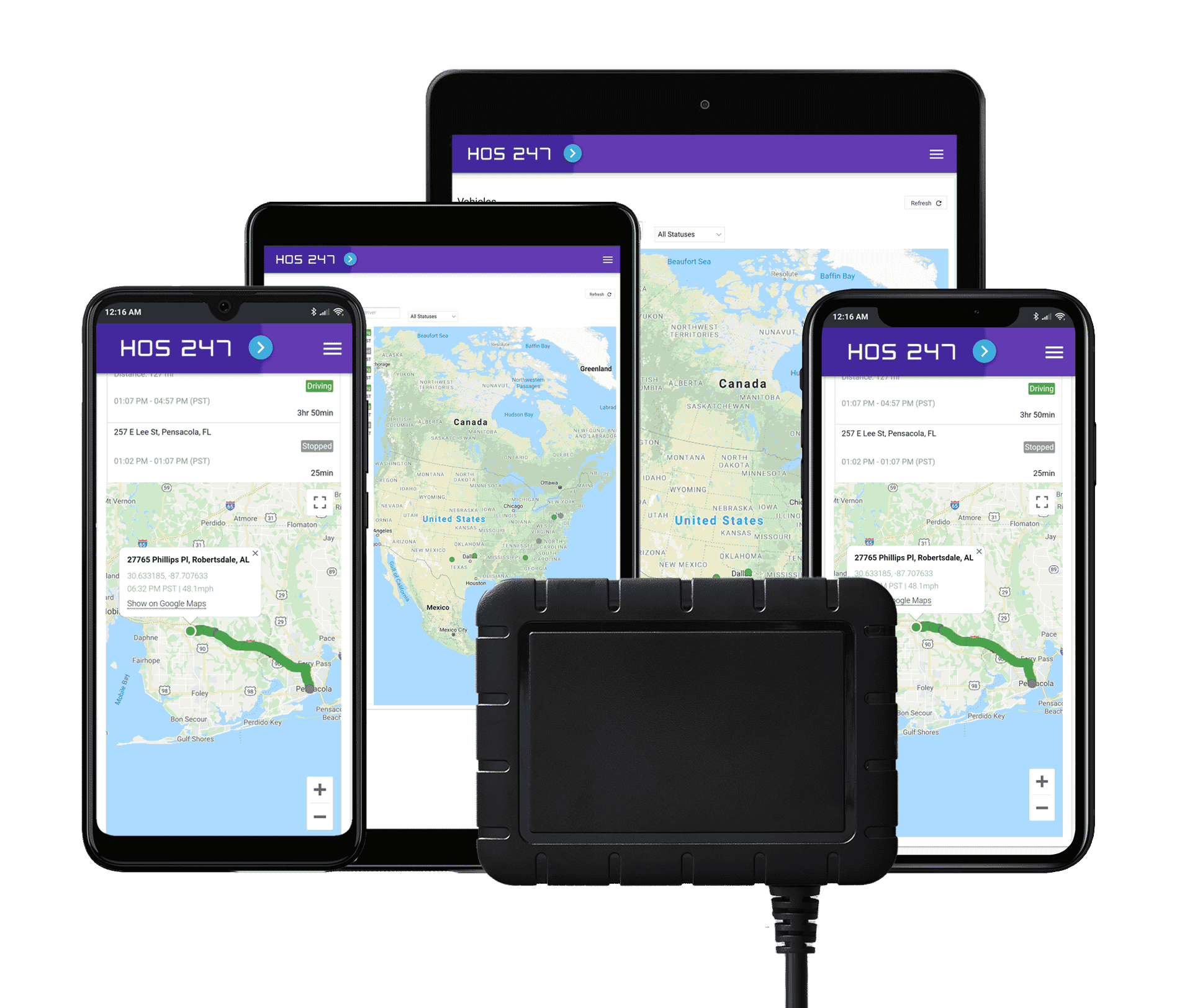
GPS Tracking
With real-time GPS tracking that updates every two seconds, fleet managers and dispatchers get a birds-eye view of their entire operations. Using one easy-to-read map, users can:
- See which drivers are available according to their hours of service, and what type of vehicle or trailer they drive.
- Make sure drivers are on schedule, allowing ETAs to be accurately shared with customers waiting for delivery and pickup.
- View data such as speed and fault codes for each vehicle.
- Eliminate guesswork and the need to perform check-in calls when drivers are on the road.
IFTA Mileage Reporting
Accurate mileage reporting is vital for IFTA compliance, but it can be a cumbersome task. HOS247 streamlines this process, minimizing administrative burdens and reducing the potential for human error. With precision, our ELD system automatically calculates distances traveled within each jurisdiction, ensuring meticulous IFTA mileage reporting without the hassle.
Idle Time Management for Fuel Efficiency
Excessive idling not only consumes fuel but also impacts the environment and operational costs. HOS247’s ELD system actively monitors and reports idle times, empowering fleet managers to optimize fuel efficiency. By identifying and addressing unnecessary idling, our solution contributes to cost savings and reduces the environmental footprint.
Proactive Fault Code Detection
Timely detection of vehicle issues is crucial for maintenance and operational efficiency. HOS247’s ELD doesn’t just track hours; it actively monitors for engine fault codes. When an issue arises, the system promptly notifies both drivers and fleet managers. This proactive approach allows for swift intervention, minimizing downtime, and ensuring that vehicles are in optimal working condition.
HOS247 Customer Care Policies
Drivers and carriers rely on us for approved ELDs that comply with DOT log book regulations and for high-quality service. Several factors distinguish us from the competition, ensuring a seamless customer experience:
- Transparent pricing. We prioritize transparency, providing a clear pricing structure without any hidden costs.
- Flexible contracts. Say goodbye to lengthy commitments. Our service comes with no long-term contracts, offering you the freedom to adapt your subscription as needed.
- Dependable hardware. Our reliable hardware is designed to work effortlessly with your drivers’ existing mobile devices, whether smartphones or tablets. This eliminates the need for expensive proprietary hardware, ensuring a cost-effective and user-friendly solution.
- Risk-free trial. We stand by the effectiveness of our ELD and app. If, within two weeks, you discover that they don’t align with your fleet’s needs, we offer a hassle-free return policy, underscoring our commitment to your satisfaction.
By choosing HOS247, fleets not only comply with the ELD mandate but also gain access to features that promote growth and success in the competitive trucking industry. Our dedication to innovation and customer support positions us as a trusted partner for fleets aiming to achieve operational excellence.

Key Compliance Tips for Navigating ELD Regulations
Having explored the intricacies of ELD regulations and introduced HOS247 as a robust solution for meeting these requirements, it’s clear that regardless of the logbook solution you choose, proactive steps towards compliance are paramount. Here are essential tips to maintain compliance and avoid potential pitfalls:
- Stay updated. Keep abreast of the latest FMCSA regulations and updates regarding ELDs and HOS to ensure your operations always comply with current laws.
- Regular training. Conduct frequent training sessions for your drivers and administrative staff on how to use elogs effectively and comply with logging requirements.
- Conduct audits. Regularly audit ELD records to identify and rectify discrepancies. This proactive approach can help prevent violations during inspections.
- Ensure device compliance. Use devices approved by the FMCSA and check periodically to ensure they remain on the registered devices list.
- Maintain ELD functionality. Regularly inspect and maintain ELDs to ensure they are in working order, recording accurately, and securely mounted.
- Develop a reporting process for issues. Have a clear process for drivers to report ELD malfunctions and know the protocol for reverting to paper logs if necessary.
- Backup documentation. Encourage drivers to keep paper records as a backup for the last 7 days, which can be critical if electronic logs are questioned or in case of a device failure.
- Understand and use exemptions wisely. Be knowledgeable about ELD exemptions and ensure they are applied correctly and in compliance with regulations.
- Promote open communication. Foster an environment where drivers feel comfortable reporting compliance concerns or suggesting improvements.
- Leverage ELD data for compliance. Use the data collected by ELDs for compliance audits, identifying areas for improvement in hours of service management, and enhancing overall fleet safety.
By integrating these compliance tips into your daily operations, you can help ensure that your fleet remains compliant with DOT regulations, thereby avoiding fines and enhancing the safety and efficiency of your operations.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











What is an ELD or electronic logging device? The FMCSA introduced this hardware device which allows truck drivers the ability to record hours of service data electronically. The ELD or electronic logging device must be connected directly to the engine

Reliable electronic logging devices (ELDs) have become essential equipment for today’s truckers. Since the federal mandate took effect, these devices have moved from optional technology to required tools for staying compliant and running efficiently. The ELD mandate changed how you

With the elog mandate in effect, business owners risk facing serious penalties and expensive fines for non-compliance, so the reliability of an electronic logging device has become one of the most crucial aspects to consider. Are you a motor carrier
