What is the ELD mandate for truckers? What are the best electronic logging devices? This article will explain the mandate, its requirements, the technology behind electronic logbooks, and their impact on hours of service (HOS) regulations. We will also give you tips on choosing the right electronic logging system for your needs and discuss how this technology is evolving and impacting the industry. Whether you’re a driver, fleet manager, or carrier owner, this guide will help you stay compliant with regulations and possibly improve your trucking operations.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
What Is ELD?
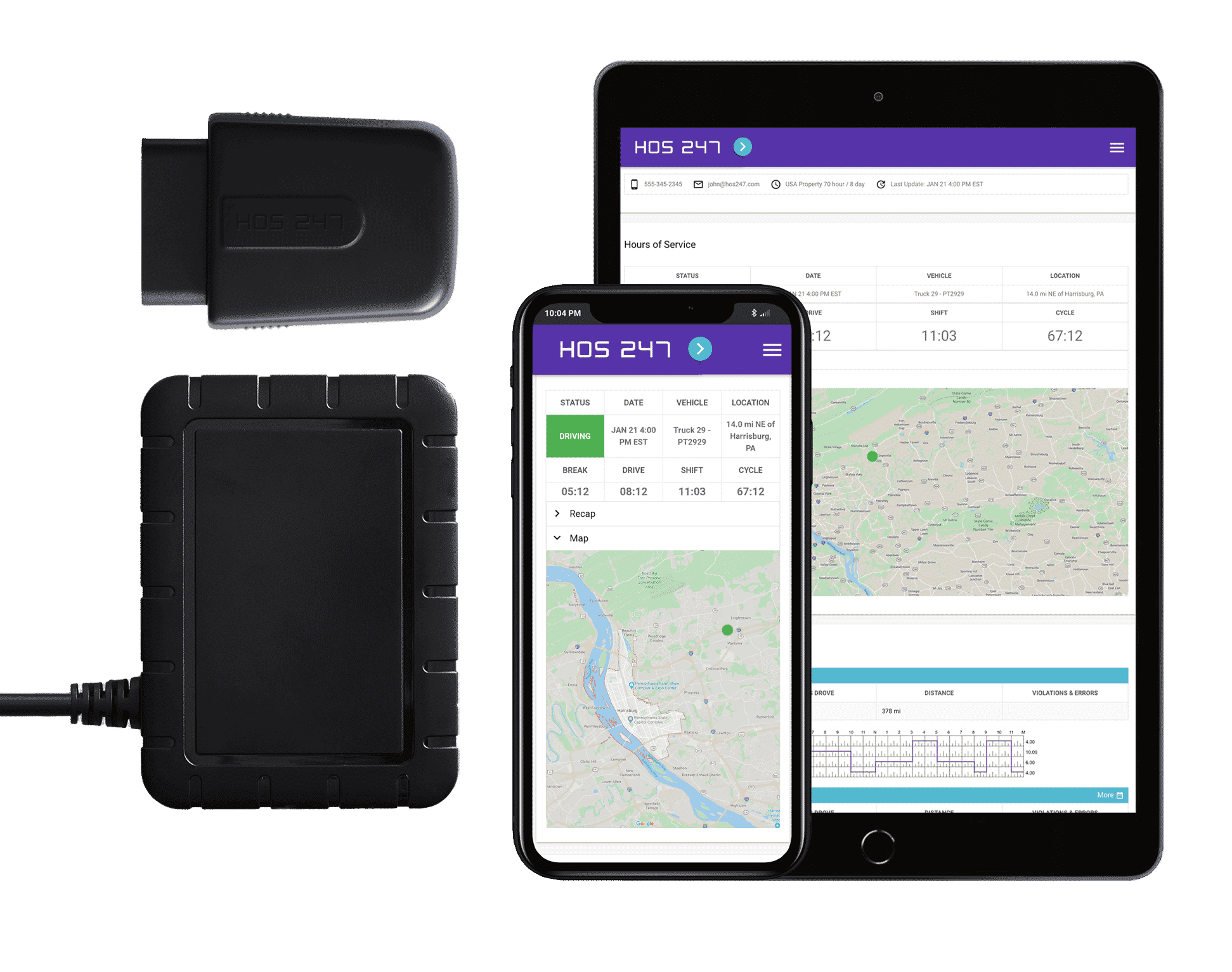
An electronic logging device (ELD), also called elog or electronic logbook, is a piece of hardware that connects to a vehicle’s engine to automatically record driving time and other aspects of HOS records. The hardware connects to the engine control module (ECM) of the vehicle through the diagnostics port. The device then synchronizes with the engine and the collected data can be accessed by the driver via an app on their tablet or smartphone and by the fleet manager through an online portal. DOT officers can review drivers’ logs through the federal electronic repository called electronic record of duty status (eRODS).
Electronic logging devices provide important information needed for regulatory compliance and fleet management, including includes:
- Date, time, and location information
- Engine hours
- Vehicle miles
- Identification information for the driver, authenticated user, vehicle, and motor carrier
- Duty status changes (On-duty, Off-duty, Driving, Sleeper Berth)
- Engine on and off events
- Vehicle motion status
ELDs are designed to reduce paperwork, improve accuracy in logging, and make it easier for authorities to enforce HOS regulations.

What Is the ELD Mandate for Truckers?
The ELD mandate for truckers is a regulation passed by the United States federal government stating that commercial vehicle drivers are required to use electronic logging devices to keep records of duty status. According to the mandate, paper logs and automatic on-board recording devices (AOBRD) had to be replaced with registered electronic logbooks before the final compliance date, which was December 16, 2019.
The mandares requirements also include:
- Data transfer. ELDs must be able to transfer data to law enforcement officers during roadside inspections. This can be done electronically or by displaying the information on a screen.
- Supporting documents. Drivers still need to keep supporting documents, like bills of lading, for their records. They must also keep the following documents in cabin:
- Elog user manual
- Datasheet illustrating RODS data transfer process
- Instructions on ELD malfunction reporting
- Blank graph grid paper
- Retention of records. Carriers must keep elog records and supporting documents for at least 6 months.
- Device registration. The device must be self-certified by the provider and registered with the FMCSA (Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration).
- Malfunction procedures. There must be a plan in place for what to do if the ELD malfunctions.
- Preventing harassment. The ELD rule includes provisions to prevent carriers from using elog data to harass drivers.
Understanding these requirements helps ensure you’re following the rules and using your electronic logbook correctly. Remember, staying compliant not only avoids fines but also helps keep the roads safer for everyone.
Who Must Comply with the ELD Mandate?
The ELD mandate for truckers has affected millions of truckers across the U.S. who are required to maintain RODS to prove compliance with HOS rules, including those domiciled in Mexico and Canada. Buses and trucks used for interstate commercial transportation come under the radar of this federal legislation. However, the FMCSA has allowed certain exemptions, which include:
- Short-haul drivers. Drivers who operate within a 150 air-mile radius of their home terminal are not required to use electronic logbooks.
- Eight-day record exemption. Some commercial drivers keep RODS for 8 days or even less out of a 30-day period. Those drivers can enjoy an exemption from the mandate.
- Driveaway-towaway operations. When the driver is operating a vehicle that is the product being shipped, the elog rule is not applicable.
- Old model vehicles. Vehicle engines manufactured before the year 2000 are not compatible with elog technology, so they are exempt from the requirement.
HOS Rules and Regulations
Hours of service regulations are designed to prevent driver fatigue by limiting the number of driving hours per day and week. The main HOS rules for property-carrying drivers are:
- 11-hour driving limit. Drivers may drive a maximum of 11 hours after 10 consecutive hours off duty.
- 14-hour limit. Drivers may not drive beyond the 14th consecutive hour after coming on duty, following 10 consecutive hours off duty.
- Rest breaks. Drivers must take a 30-minute break when they have driven for a period of 8 cumulative hours without at least a 30-minute interruption.
- 60/70-hour limit. Drivers may not drive after 60/70 hours on duty in 7/8 consecutive days.
Drivers can forgo these rules in specific cases. These exceptions include:
- Adverse driving conditions. Drivers may extend the 11-hour maximum driving limit and 14-hour driving window by up to 2 hours when encountering adverse driving conditions.
- Short-haul exception. Certain short-haul drivers may qualify for an exception from the 30-minute break requirement and may be allowed to use a time record instead of a logbook.
- 16-hour short-haul exception. Once per week, a driver may extend the 14-hour driving window to 16 hours, provided they return to their work reporting location that day.
Whether you’re a solo owner-operator or managing a large fleet, understanding these rules is crucial. For the most current and accurate information on ELD regulations, truckers should regularly refer to the FMCSA’s official website.
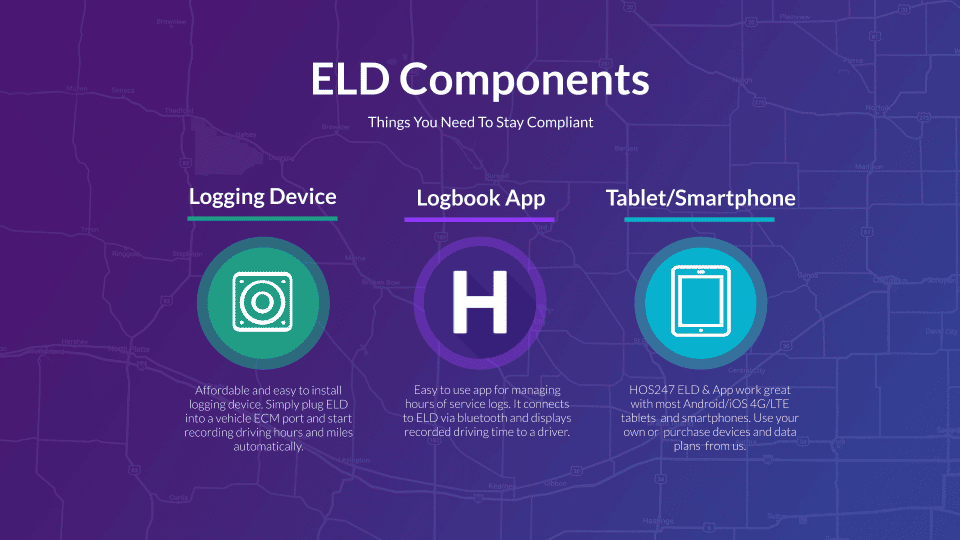
Choosing the Right Electronic Logging Device
Some truckers might not be satisfied with their choice of logbook. To help them make the right pick for a switch, here are some key characteristics to identify a quality electronic logbook:
- FMCSA registration. Verify that the electronic logbook is registered with the FMCSA. While registration doesn’t guarantee compliance, it’s a necessary first step. You can check the FMCSA’s website for the current list of registered ELDs.
- User ratings and reviews. Check user ratings on platforms like the Apple App Store or Google Play Store. Look for providers with positive reviews, particularly regarding logbook functionality and customer service. Aim for a rating above 4 out of 5.
- Ease of use. The ELD should have an intuitive interface that’s easy for drivers to navigate and use while on the road.
- Compliance updates. Choose a provider that regularly updates their system to stay compliant with changing regulations.
- Integration capabilities. Consider how well the ELD integrates with your existing fleet management systems or other software you use.
- Data accessibility. Ensure the system provides easy access to logs and reports for both drivers and fleet managers.
- Additional features. Consider what additional features, such as GPS tracking or IFTA calculations, might benefit your operations.
Ultimately, finding the right logbook is a decision that can help your fleet’s efficiency, compliance, and bottom line. By prioritizing your specific needs, you can choose a system that not only helps you achieve compliance but also adds value to your operations.

Benefits of HOS247 Electronic Logging Devices
HOS247 is a reliable provider with a proven track record. Besides testing our solution periodically for FMCSA compliance, we offer additional features to help fleet managers and owner-operators increase efficiency and profitability. The main benefits of partnering with HOS247 are:
- Reliable hardware. The quality HOS247 electronic logging devices means they are durable and won’t break down mid drive and it makes for a stable Bluetooth connection. It can be installed in minutes and starts recording information immediately after being switched on.
- User-friendly elog app. Our logbooks are designed to work on Android or iOS smartphones and tablets. The HOS247 app allows drivers to manage HOS records, create DVIRs, and transfer RODS with a few clicks.
- Intuitive portal for fleet managers. Fleet managers have access to the intuitive online portal to access vehicle and driver information in real time.
- Top-rated multilingual support. HOS247 has an active support team available any day of the week to help you troubleshoot and answer your questions. We speak English, Spanish, Russian, and Polish.
- Add-on features. Our system can be complemented with additional features such as GPS tracking, vehicle diagnostics, idling monitoring, and IFTA mileage calculations.
- Flexible no-contract policy. We have a no-contract policy to offer customers the flexibility they need. Our clients decide to stay with us because of the quality of our services and not because of lengthy contracts. Our monthly plans can be upgraded, downgraded or canceled at any time. Truckers can also choose to pay annually.
- 14-day trial period. Every new customer can get a two-week trial period. Truckers can use the ELD for 14 days and return it for a full refund if they are not satisfied.
Additional Information About the ELD Mandate
The ELD mandate has significantly changed the trucking industry, and it’s crucial to understand its broader effects. First and foremost, the FMCSA takes compliance seriously. Breaking these rules can lead to fines, hurt your CSA scores, and even affect your right to operate. In extreme cases, drivers or vehicles might be taken off the road. It’s worth noting that both drivers and companies can be held responsible for elog violations.
Along with compliance concerns, the move to electronic data has raised questions about privacy. To address these issues, the mandate includes specific rules to protect drivers’ personal information. As part of this effort, companies must have policies in place to keep ELD data safe from unauthorized access.
While compliance and privacy are important, the main goal of DOT regulations is to improve road safety. Encouragingly, it seems to be working. Recent studies show that since electronic logbooks were introduced, there have been fewer hours of service violations and fewer crashes. This suggests that the technology is indeed helping to make roads safer for everyone.
Despite these benefits, the transition hasn’t been without challenges. Many in the industry initially found the switch to ELDs difficult. However, after an adjustment period, drivers and companies often report unexpected advantages. They say electronic logs have helped reduce paperwork and streamline operations. As with any significant change, it takes time to adapt, but the long-term benefits for safety and efficiency are becoming increasingly clear.

Integration of ELDs with Other Technologies
Electronic logbooks have become a standard tool in the trucking industry, but their impact goes beyond just recording hours of service. As technology advances, ELDs are increasingly working together with other systems to create smarter, more efficient trucking operations. Here’s how:
- Connecting with fleet management systems. Electronic logbooks now work with systems that manage entire fleets. This allows for real-time tracking, better route planning, and monitoring of fuel use and maintenance needs.
- Advanced data analysis. New software can analyze elog data to identify patterns. It can predict potential maintenance issues or when a driver might be approaching HOS limits.
- ELDs and autonomous vehicles. As self-driving truck technology develops, ELDs provide valuable data on human driving patterns. This helps improve autonomous systems and manage the transition between human and computer control.
- Mobile and cloud technology. Modern electronic logging systems use mobile and cloud technology to share information in real time. This improves communication between drivers, dispatchers, and managers.
As we’ve seen, ELDs are no longer standalone devices but are becoming part of a larger, interconnected system in the trucking industry. This integration with other technologies is creating new opportunities for efficiency, safety, and profitability.

Conclusion
The ELD mandate for truckers has significantly changed the industry. Understanding and effectively using electronic logbooks is crucial for success in modern trucking.
Electronic logs are also part of a broader technological shift in trucking. They work alongside other new technologies to enhance fleet management and logistics. However, it’s important to remember that technology is just a tool. The key to success lies in how well trucking companies adapt to these changes, train their staff, and use ELD data to make informed decisions. As the industry evolves, choosing a dependable fleet management provider will also help carriers to remain competitive and compliant.
By embracing these technologies wisely, trucking companies can do more than just meet regulatory requirements. They can improve efficiency, enhance safety, and increase profitability. The future of trucking is increasingly digital and connected, with ELDs playing a central role in this transformation.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











In today’s dynamic business environment, where efficient operations and cost savings are crucial, fleet tracking has become a vital solution for trucking businesses. This technology uses GPS and advanced fleet management systems to monitor and manage vehicles in real time,

In today’s fast-paced business world, managing a commercial fleet can be challenging, but it doesn’t have to be. With the help of fleet management systems, carriers can enjoy various benefits, such as reducing fuel costs, enhancing driver safety, providing better

In today’s fast-paced business world, effective asset management is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Companies across various industries rely on their assets, such as vehicles, equipment, and inventory, to keep their operations running smoothly. However, managing these assets can