The new federal mandate for the use of HOS ELDs will help keep drivers compliant with driving and on-duty time limits. Driver fatigue has proven to cause accidents and losses—human, material, and economic. The government created HOS rules to deal with this problem; soon, elog devices will be the required way for drivers to maintain accurate records of duty status and trucking companies can benefit from implementing them before the due date.
Transport Canada and the Ministry of Transport have set guidelines for RODS and will monitor drivers and carriers to ensure compliance. In this article, we will look at how the HOS log book fits into the trucking industry and how to be ready for the incoming mandate.
ELD Mandate Enforcement Timeline
The mandate states that all commercial motor vehicle drivers will be required to keep records of their duty status using an electronic logbook. This means that drivers will need electronic logging devices to comply with the Ministry of Transportation regulations. In Canada, the elog mandate has followed a progressive rollout, following several steps:
- December 2017 – The government published a series of regulations for commercial vehicle drivers’ hours of service, including electronic logging devices.
- June 2019 – Transport Canada announced the mandatory use of electronic logbooks for operations involving commercial trucks and bus operators.
- June 2021 – Original deadline for truckers to switch from paper daily logs and comply with elog requirements. Instead, a progressive enforcement period began.
- June 12, 2022 – Second enforcement deadline. This delay implied that carriers would not be penalized for using paper logs until this date. However, there was a second delay due to the lack of sufficient certified devices.
- January 1, 2023 – Updated full enforcement deadline. As of this date, carriers must use ELDs and have completely phased out paper logs, unless they fall under an exemption category.
After this last date, drivers and carriers found to be non-compliant may be subject to penalties. Transportation authorities will have the power to issue corrective measures and even revoke the enabling transportation certification if the new regulations are not observed.
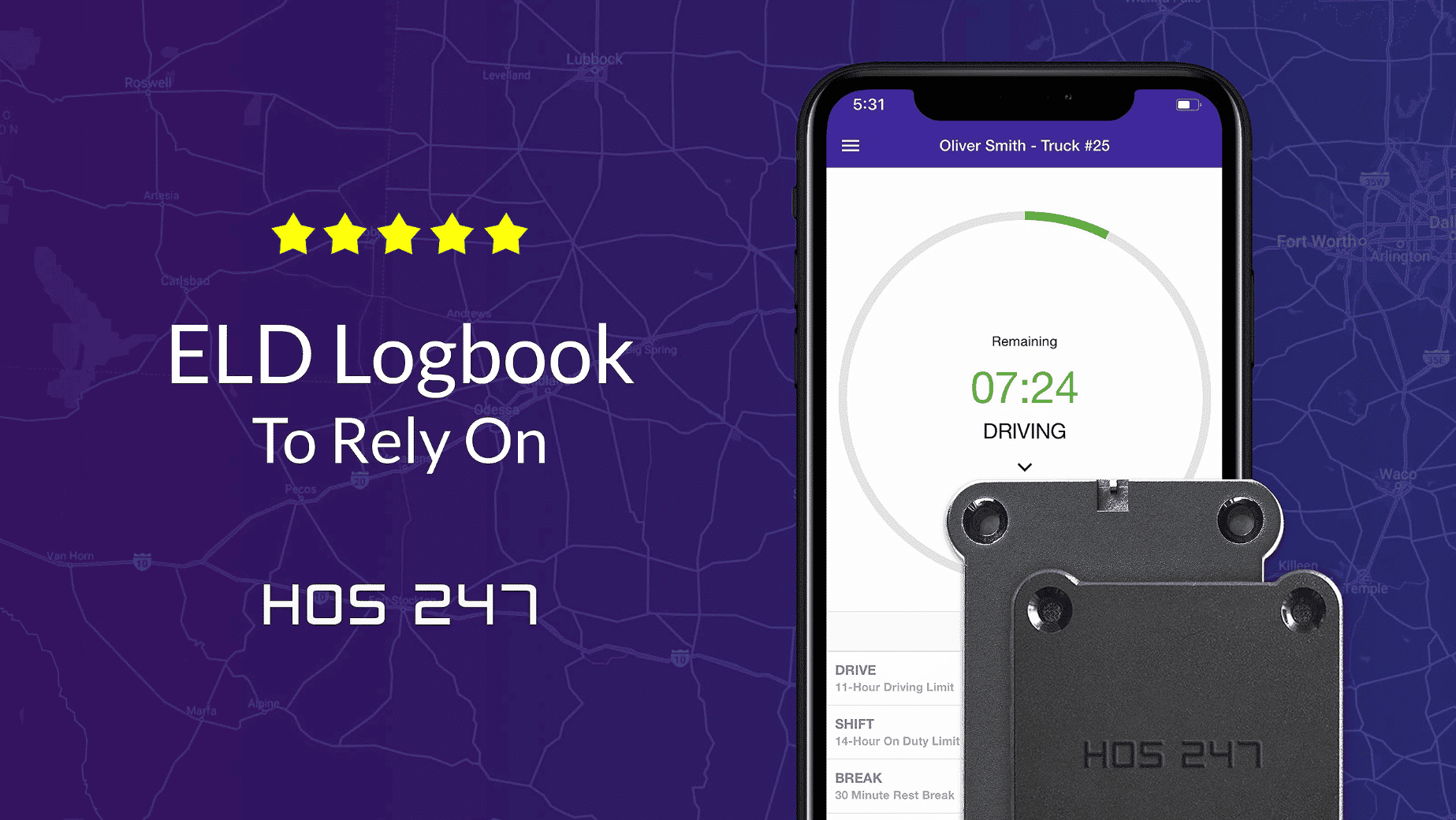
HOS247 Is a Leading ELD Service Provider
HOS247 has developed a dependable HOS log book to manage RODS and enhance trucking businesses’ performance. We offer customers an electronic logbook that combines quality hardware and a user-friendly ELD HOS app to streamline recordkeeping and increase profitability. Our additional features, customer service, and dedication to being a trustworthy business partner bring additional value to our product. Here are some of the most popular benefits of our elog solution:
- Reliable hardware. Our hardware has been put to the test to make sure that it performs optimally at all times. The HOS247 electronic logbook is tamper-resistant, reliable, and operates with a stable Bluetooth connection to provide accurate, real-time data collection.
- Compatible ELD HOS app. Our HOS log book app runs smoothly on both Android and iOS smartphones and tablets, adjusting to the driver’s preference and simplifying fleet management.
- Top-rated customer service. We offer top-rated technical support in English, Polish, Russian, and Spanish every day of the week to keep close contact with our clients.
- Trial-period. HOS247 offers a trial period of two weeks so truckers can try out the HOS247 elog system in real operations. If you are not satisfied, you may return the device within this time and receive a hassle-free refund.
- No-contract policy. Our services can be purchased on a monthly or yearly subscription, there is no need for extended commitments. This way, you can add features or scale your plan up or down according to the specific needs of your business.
- Extra features. To complement our HOS ELD solution, we optimize and automate tasks such as IFTA calculations and idle time reports. We also include GPS tracking and vehicle maintenance to prevent breakdowns and extend vehicle life.
Canadian Mandate Exemptions
Transport Canada’s mandate applies to most commercial vehicles, but there are some specific circumstances in which the use of HOS ELDs will not be necessary. There are four key exceptions to the Canadian ELD rule:
- Special permit exemption. A territorial direction office may issue a special permit that enables a vehicle to operate outside the scope of the mandate.
- Statutory exemption. A provincial or territorial government may also issue a statutory exemption, which excludes the vehicle from supervision by Transport Canada.
- 30-day rental (or shorter). Vehicles operating under a short rental agreement (30 days or less) are exempt from the mandate. Note that this exemption will not be renewed if the rental is extended.
- Manufacturing date. Vehicle models prior to the year 2000 are also exempt from the ELD mandate. These engine models are not compatible with HOS ELDs, so the mandate allows them an exception.
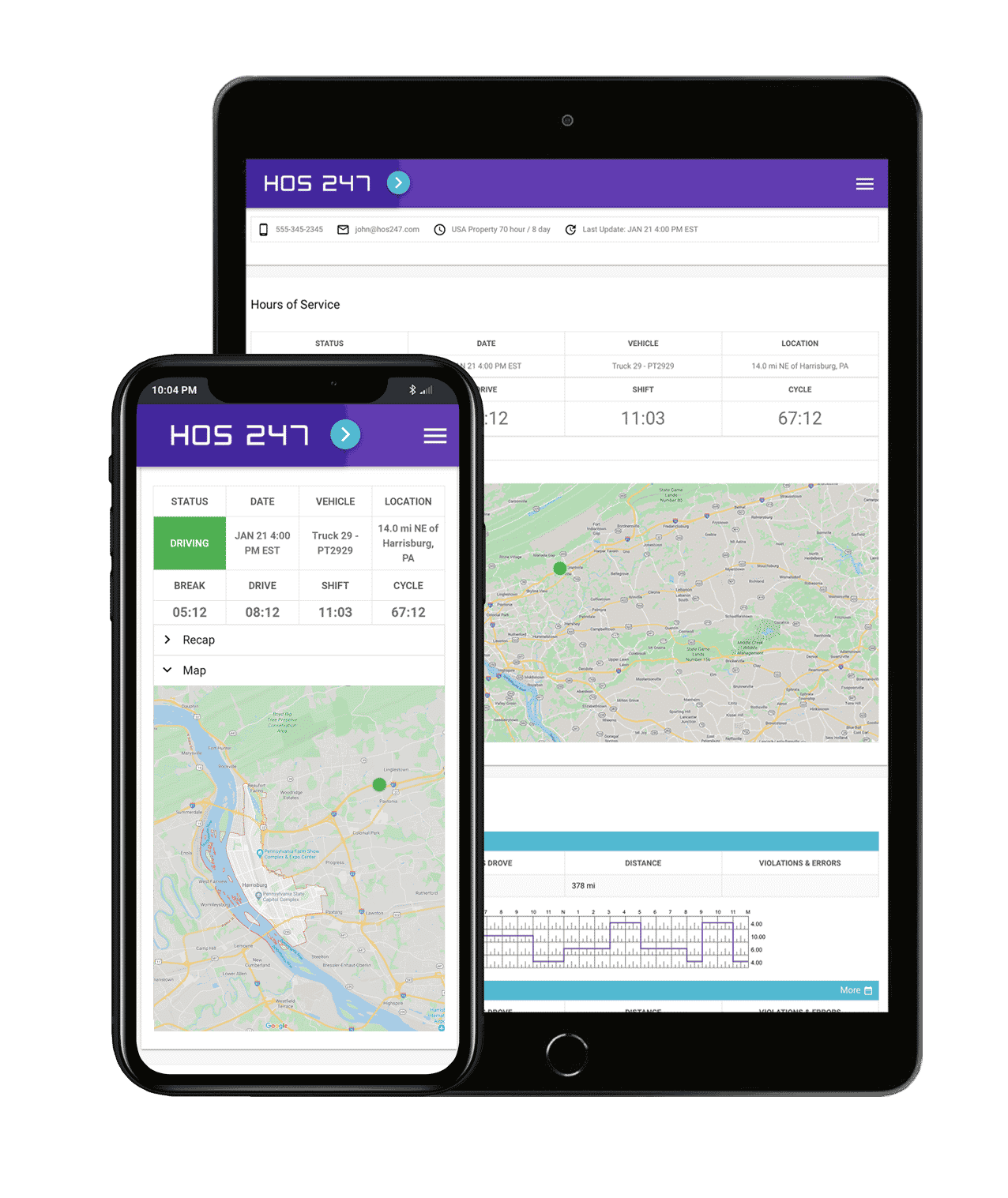
Key Requirements of the Mandate for an HOS ELDs
There are several standards in the Canadian mandate that are specific to HOS ELD solutions. An ELD HOS app must support these key requirements to be compliant:
- Prior certification. Elog providers will require a third-party certification for their device to be compliant.
- Strict distance limits. Drivers are allowed 75 kilometers for personal use.
- Off-duty time. ELD HOS rules allow drivers to take 2 off-duty hours within a 16-hour driving window.
- Driving status updates. Driving status must be updated automatically when the electronic logging system detects a vehicle speed of 8 km per hour or more. When the engine stops for 5 minutes, the device must prompt the driver to confirm whether the status needs to be changed to “off-duty”. The logbook needs to be activated to ‘yard move’ mode when driving within a customer’s yard to prevent the driver’s ‘on-duty’ status from changing to ‘off-duty’.
- Vehicle diagnostics capabilities. The registered HOS ELD must be capable of detecting minor and major faults in the vehicle.
- RODS management option. Drivers must be able to manage unassigned driving time to comply with ELD HOS rules, accepting or rejecting said time. Drivers must be able to manage or edit (and annotate) any changes made to the HOS log book.
HOS247 Supports Canadian HOS Rules
Responsible providers offer effective ELDs HOS management solutions to fulfill all legal requirements. HOS247 provides a HOS log book that integrates an intuitive interface and efficient technology to meet federal standards and benefit trucking businesses’ bottom lines. Our devices are dependable for compliance, improve operations and enhance productivity.

The electronic logbook also supports updated ELD HOS regulations like the 60th parallel limits. Canadian rules apply in different ways for operations taking place in the northern and southern parts of the country. The rules on both parts of the country are structured in a similar way, but there are some critical differences:
- When operating North of the 60th parallel:
- Drivers can choose to work under one of two cycles:
- Cycle 1: 80 hours in 7 days.
- Cycle 2: 120 hours in 14 days.
- Driving time is limited to 15 hours daily or in a single shift. Past this point, drivers must take a break of at least 8 (consecutive) hours off-duty before they can go back to driving.
- No driving is allowed after 18 hours on-duty.
- No driving is allowed after 20 hours have passed since the last 8-hour period off-duty.
- Yard move, adverse driving, and personal conveyance statuses are supported.
- Drivers can choose to work under one of two cycles:
- When operating South of the 60th parallel:
- Drivers can choose to work under one of two cycles:
- Cycle 1: 70 hours in 7 days.
- Cycle 2: 120 hours in 14 days.
- HOS may be restarted or switched by
- Taking 36 off-duty hours (uninterrupted) for Cycle 1.
- Taking 72 off-duty hours (uninterrupted) for Cycle 2.
- After every 14-day cycle concludes, drivers must be off duty for 24 consecutive hours at least.
- Driving time is limited to 13 hours a day. Drivers must take at least 8 off-duty hours in a row after this time before driving again.
- After 14 hours on duty, drivers may not drive but may carry out non-driving activities. Driving is allowed again after 8 hours spent off duty.
- No driving is allowed after 16 hours have passed since the last 8-hour period off-duty.
- Daily off-duty time must be at least 10 hours.
- Off-duty time (outside of the 8 consecutive hours) may be spread throughout the day in blocks of 30 minutes.
- Yard move, adverse driving, personal conveyance, and off-duty time deferral statuses are supported.
- Drivers can choose to work under one of two cycles:

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











As per the ELD mandate, commercial vehicles will soon require electronic logging systems to stay Transport Canada compliant. An efficient elog solution will be essential for trucking businesses to thrive once the mandate is fully enforced beginning 2023. In this

GPS fleet tracking has become an essential tool for modern fleet management, revolutionizing how trucking companies operate and manage their vehicles. By providing real-time location data and valuable insights into vehicle performance, GPS trackers help fleet managers improve safety, optimize

Truckers have a lot to consider when choosing an electronic logbook for their business. They need to be mindful of compliance, price, the user-friendliness of each logbook app, and more. Considering the high turnover rate among drivers, it is vital