If you drive a commercial vehicle, your elog system is not just a tool; it’s a necessity for every trip. The safety and rule-following of your operations depend heavily on the quality of your ELD system, so it must be chosen carefully. A key part of the system will be the drivers daily log book app. Most providers offer bring your own device (BYOD) solutions, meaning drivers can use their own smartphone or tablet to run the elog app. This article will guide you through everything about app compliance, keeping logs correctly, and penalties for non-compliance to help you keep your business on track.
Are Daily Log Book Apps Compliant with the Elog Mandate?
Downloading elog mobile apps from an app store is easy, but it it not enough to be compliant. To meet DOT requirements, truckers need a tamper-resistant device that connects to the vehicle’s engine to record HOS data. The information it collects is then sent to the drivers’ mobile device through the app. Truckers need their vehicle daily log book device to be FMCSA-approved to comply with the ELD mandate. This approval means the app is okay to use as part of this system, but not by itself.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
HOS247 Is a Top-Rated Drivers Daily Log Book App Provider
At HOS247, we are dedicated to offering a reliable vehicle daily log book backed up by top-rated customer support to help our clients run their trucking operations more efficiently. We see ourselves not just as a service provider, but as a strategic partner committed to help your business grow.
Our commitment to quality is reflected in the positive feedback from our users and high ratings on app stores. Our clients appreciate our easy-to-use drivers daily log book app, and numerous benefits, including:
- Reliable and easy-to-install hardware. Our device is durable and has been designed for easy and quick installation. Simply connect the device to the diagnostics port and sync to the driver daily log book software via Bluetooth and the system will be set and ready.
- Driver-friendly logbook software. HOS247’s interface is easy to use and quick to learn. The logbook operates just as well on Android and iOS devices, catering to all driver preferences.
- Top-rated support. Available Monday through Sunday, our technical support team is well trained and multilingual, speaking English, Spanish, Russian, and Polish. Our callback policy ensures prompt attention to any issues even if the call drops.
- Trial period.Try our logbook for two weeks to see how it fits into your workflow. If it’s not the right fit, return it within this period for a full refund, no questions asked.
- Flexible payment options. Pay on a monthly or annual basis. Monthly plans can be scaled up or down as you see fit.
- No contract policy. At HOS247, we don’t believe in binding our customers with long-term contracts. Instead, we let you decide how long you want to stay with us. Our confidence in the quality of our solutions means we’re committed to giving you the control to choose what works best for your business.
- Extra features. Enhance your electronic logbook experience with additional features like real-time GPS tracking, vehicle diagnostics with fault code detection, IFTA mileage calculations and more.
HOS247 is not just about providing a product; it’s about delivering an effective solution that supports and grows with your trucking business.
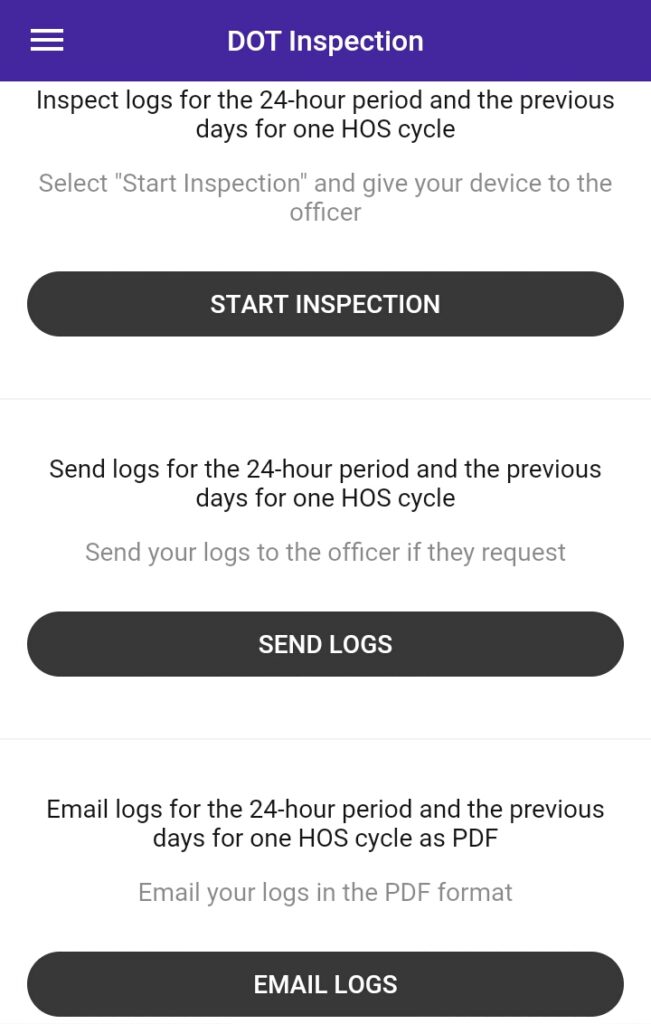
Can ELD App Records Be Edited?
The vehicle driver log book will record all the time that a vehicle is in motion as driving time; this data cannot be changed to non-driving time. That said, occasionally, something needs to be cleared up. There are two kinds of changes that can be made to the log:
- Edit. These are changes made to the information in an ELD record. However, driving time recorded when the vehicle is in motion cannot be altered to non-driving time.
- Annotation.These are textual notes added to a record, update, or edit. They are required for all edits to provide context and justification.
Authorized individuals, like drivers or staff, can make these changes. But remember, the original records remain intact even after edits and annotations. Drivers are responsible for:
- Reviewing and ensuring the accuracy of changes.
- Justifying and signing off any edits made by staff.
- Resubmitting the updated electronic logs.
ELD-Related Fines and CSA Scores
There are 22 violations related to the use of logging devices and their drivers daily log book app that affect a carriers’ CSA score. Here are some of the most common:
- Failing to use the correct method to record HOS. Up to 7 points.
- Incomplete logs or errors. These can cost as much as 5 points. These include failing to document a device malfunction or not setting up the screen to be visible from outside the vehicle.
- Lesser violations. These add up one point: not having the ELD manual available, not certifying logs, missing information that needs to be input manually such as shipping documents or location descriptions.
Fees for recordkeeping-related violations are around $1,307 on average in a single day. The highest of these penalties is $13,072 for knowingly falsifying vehicle driver log records. Some of these violations will also get drivers put out of service. These include falsifying logs, not using an elog while being outside of the exemption categories, or using unauthorized logbooks.
As seen above, fines can be extremely expensive. A reliable device with user-friendly logbook software can go a long way in making sure drivers keep their records properly to save time and money.

Best Practices for Vehicle Driver Log Book Use
Implementing a log book system isn’t just about compliance—it’s also about maximizing efficiency and safety in your operations. Here are some best practices to ensure you’re getting the most out of your ELD system:
- Regular training and updates. Keep drivers and administrative staff informed about the latest ELD updates and regulations. Regular training sessions can help in understanding the nuances of the vehicle driver log book app and hardware.
- Data management and security. Elogs collect a significant amount of data. It’s important to manage this data securely and in compliance with privacy regulations. Implement robust data management policies to protect sensitive information.
- Compliance checks. Regularly review ELD records to ensure they are compliant with FMCSA regulations. This proactive approach can help avoid penalties and fines associated with non-compliance.
- Using ELD features. Electronic logbooks offer more than just logging hours. Use their features for route optimization, fuel consumption analysis, dispatch efficiency, and maintenance scheduling. These features can significantly enhance profitability.
- Dealing with technical issues. Having a technical support team readily available can minimize downtime and facilitate operations. Make sure your provider offers such a team. If it doesn’t, it might be time to switch.
- ELD integration with other systems. Integrate your ELD with other fleet management systems for a comprehensive view of your operations. This integration can streamline processes and provide valuable insights for decision-making.
- Regular feedback from drivers. Drivers are the primary users of the log book. Regular feedback from them can provide insights into the system’s usability and areas for improvement.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your vehicle driver log book system is not only compliant with regulations but also a valuable tool for enhancing the efficiency and safety of your fleet operations.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
Understanding the Key Differences Between Paper Logs and Electronic Logs
The shift from paper to elogs marks a significant change in how commercial drivers record their hours of service. Here’s a closer look at the differences:
-
Automation and real-time tracking. Electronic logs automatically record vehicle activity by connecting to the engine. This automation not only saves time but also reduces human error. Drivers can access these records through a daily log book app. In contrast, paper logs require manual entry, which is time-consuming and prone to inaccuracies.
-
Efficiency and accuracy. Elogs streamline record-keeping, ensuring data is captured accurately and in real time. Paper logs, while straightforward, demand additional effort and diligence from drivers to maintain accurate and organized records.

Currently, most commercial drivers use electronic logs in accordance with the elog mandate. However, paper records are still used by drivers included in the following exemption categories:
- Short-haul exemption. Drivers who operate within a specific distance from their work location (150 air-mile radius).
- 8 day/month exemption. Drivers who keep RODS for up to eight days during a 30-day period.
- Drive-away-tow-away operations. When the vehicle being driven is the actual commodity.
- Manufacturing date. Vehicles with engines manufactured before the year 2000.
Paper records are also necessary in case of an ELD malfunction. The FMCSA states that the driver must notify the motor carrier of the issue and switch to paper logs until the device is fixed, which should not exceed 8 days.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











Ever since the ELD mandate was introduced by FMCSA, trucking companies and drivers are in a dilemma on how to choose the right provider. The e-log system has been mandated by the DOT to increase road safety and vehicle security.

Efficient logistics are crucial for business success, particularly in the trucking sector. Advanced fleet management technologies, like GPS tracking, provide carriers with methods to boost efficiency and secure a competitive edge. This article focuses on the essential process of choosing

Every minute counts when you’re on the road. In today’s trucking industry, rising costs and tighter delivery windows put extra pressure on your ability to maximize drive time. The ELD mandate changed how we track hours, but it also opened