ELD devices are essential to truckers and carriers in order to follow federal and state rules. The ELD Mandate is now in full enforcement, and most drivers and carriers must follow it. HOS247 services and technology help drivers, owner-operators, and fleet operations to adhere to complex interstate rules, intrastate regulations, and exemptions.
HOS247 Provides ELD Trucking Devices
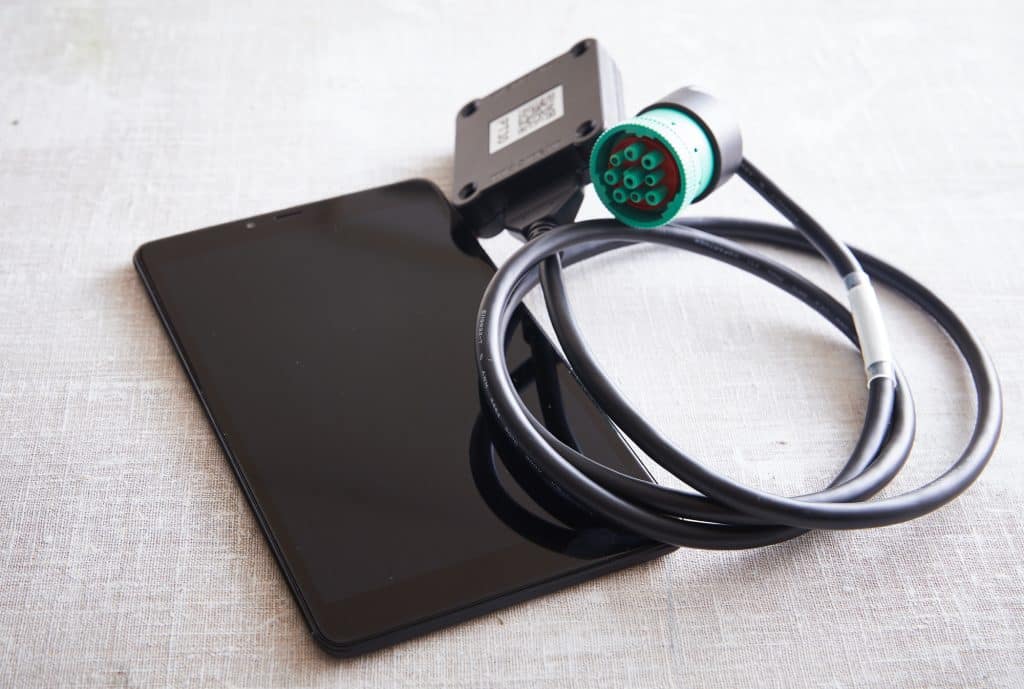
HOS247 provides reliable technology to comply with the mandated hours of service regulations. Drivers and managers can rely on customer support professionals who speak their language, whether that language is English, Spanish, Russian, or Polish. Devices pair easily with tablets via either Bluetooth or USB. The electronic truck logbook apps and other software connect in a flash to help drivers manage routes and compliance. HOS247 devices deliver all-in-one solutions with no contracts and Hassle-Free 2-Week Returns.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
Final Rule
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) is the agency that establishes standards for commercial drivers and carriers. The legislation created to enforce the use of ELDs (electronic logging devices) is called the ELD Mandate. Most commercial drivers and carriers are required to use ELD devices for trucks, as described in detail by regulations.
The legislation accomplishes four main objectives. First, it spells out the requirements and technical specifications that devices must follow. Second, it requires truckers to use devices to record RODS (Records of Duty). Third, it directs commercial drivers and carriers how to use ELD devices in their trucks in order to follow specific HOS (hours of service) rules efficiently. Fourth, it adopts rules to clarify that devices help commercial drivers and carriers rather than harass them.
Full enforcement of the Federal Mandate began on December 17, 2019. This means that most commercial drivers and carriers must have migrated from older automatic onboard recording devices to ELD trucking devices. DOT vehicle inspectors will not grant any “soft enforcement” grace periods. They will face an “out of service” violation unless they are in shorthaul rules or exemption. An “out of service” violation means that the driver carrying property does not have an approved method of logging records of duty (RODs). They are grounded for 10 hours, with passenger carriers for 8 hours. DOT inspectors will cite drivers and carriers who do not follow the requirements. Violations are costly for drivers and fleet managers.

Who Must Comply?
According to the FMCSA, the ELD Rule applies to commercial motor vehicles that are required to maintain records of duty status. Since the Final Rule began December 17, 2019, electronic logging devices (ELDs) for trucks are required for most commercial motor vehicles. The FMCSA provides many useful checklists to help drivers and carriers decide the facts about the ELD Mandate.
Types of Trucks
Trucks involved in interstate commerce weigh more than 10,001 pounds. (In kilograms, 10,001 pounds is 4536.377 kg.) The weight can include the combined weight of a truck and trailer together. The manufacturer’s rating (GVWR) is listed on a sticker on the driver’s door and is the figure that the DOT inspector usually uses for the weight of the vehicle.
If a vehicle carries harmful materials, and the DOT requires placards, it is a commercial motor vehicle, no matter what it weighs. Types of hazardous materials include explosives, gases (flammable or non-flammable), combustible liquids and solids, toxic materials, radioactive materials, and corrosive materials. If a material threatens the public or the environment, the DOT may classify it as “hazardous”.
HOS Rules
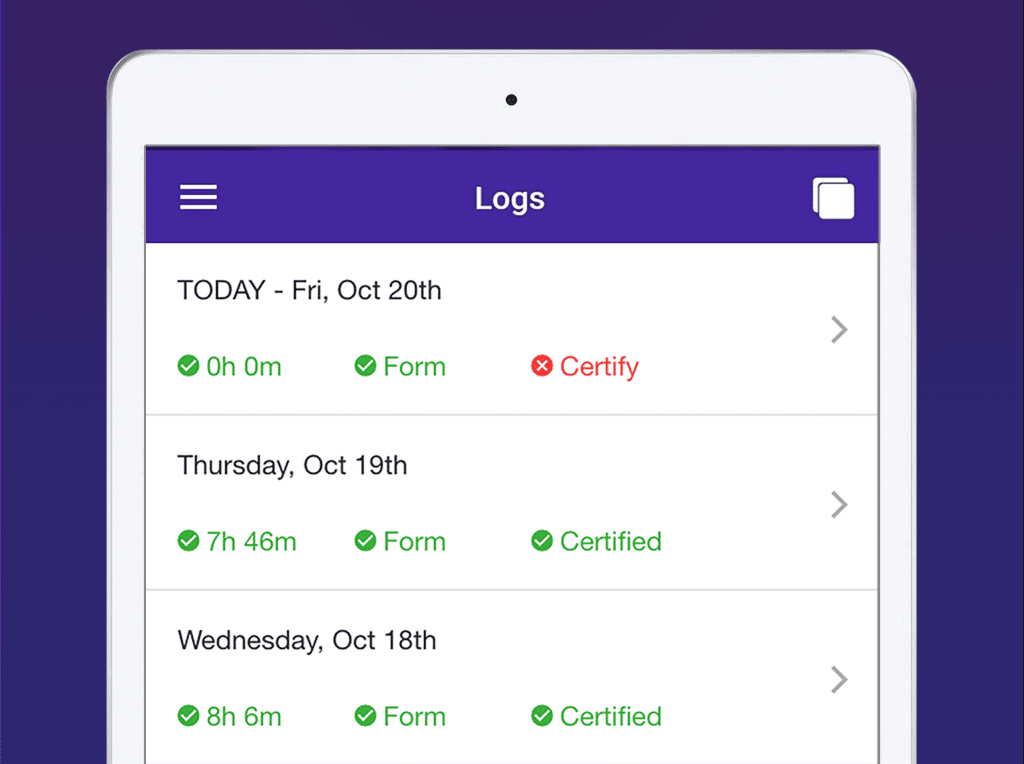
The HOS rules that govern when drivers must work, when they must take breaks, and when they must be out of service are complex. The FMCSA provided a summary of rules for most truck drivers who carry loads for hire. These rules determine the maximum of driving hours after hours not driving, the length of rest breaks and when they must occur, and the number of consecutive days in a driving “week”. ELD devices for truckers record and keep track of duty status, whether it is drive time, breaks, hours out of service, or time in the cycle.
The ELD Mandate was put into place to improve safety for truckers, as well as others on the road. The number of hours a driver can operate a vehicle are limited, and mandatory breaks are determined, to ensure that rested drivers are on the roads. Mandatory ELD trucking devices reduce the amount of paperwork that drivers and carriers keep on hand.
Exemptions
Several different types of exemptions to the rule exist. When the commodity is the truck itself, as in a “driveaway-towaway” operation, drivers can still use paper records to record their actions. Vehicles with engines manufactured before 2000 are also exempt. Some exemptions are specifically for drivers who operate closer to their home terminal area, but others apply to drivers no matter how long their route distance. Drivers with commercial driver’s licenses who drive within a 100-air mile radius from their home area do not have to hold to 30 minute breaks after 8 hours of driving time. Those drivers who do not have commercial driver’s licenses can drive within 150 miles from home. They also do not have to follow the law for 30-minute required time off after 8 hours driving.

All drivers can use an adverse driving condition exemption and extend their driving limit by 2 hours, from 11 hours to 13 hours. However, the driver must not know about the adverse conditions before they start driving. For example, sudden fog or snow would be exempted, but forecasted snow or fog would not. If the driver could have known a road would be closed before they started out, because it was marked on the DOT website, it would not fall under the 2-hour exemption, but if a road were closed en route because of an accident, then it would be an exemption. Drivers and carriers should follow trip planning based on road and weather conditions.
The FMCSA, the President, or state governors can declare an emergency, which will temporarily suspend the HOS rules. Usually the emergency declarations concern the need to get supplies to areas declared disaster areas. Regulations spell out the type of materials and supplies that are covered by the emergency exemptions.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
Interstate and Intrastate Rules
The HOS Rules and exemptions are complicated enough for interstate driving, so an ELD trucking device is needed to keep track of driver and carrier compliance. However, rules also differ within states, or driving intrastate. For example, in Texas, drivers are limited to 12-hour shifts following 8 hours out of service. They must be off duty following 15 consecutive hours of work. In addition, they are restricted to 70 hours worked or driven in any 7-day period. The 7-day periods restart after 34 or more hours off. Short-haul exemptions also apply.
Intrastate driving is driving within the same state. The state of California has decided to postpone the final rule for the ELD Mandate until December 31, 2020.
Why HOS247 is a Good Choice
HOS247 provides high quality ELD trucking devices with top-rated support. Our support team members are knowledgeable about HOS compliance and operations, as well as troubleshooting problems on the road. We are able to assist customers in English, Spanish, Russian, and Polish. HOS247 provides training to drivers on how to connect ELD devices to trucks and how to use electronic logbooks in a compliant and efficient manner, making it so much easier for fleet managers to stay on top of safety regulations. HOS247 provides a seamless transition for drivers, owner-operators, and safety managers to comply with the ELD Mandate.

I’ve co-founded, built and managed several transportation-related businesses. Now, I’m a founder and CEO of HOS247 – an AI Transportation Platform for trucking companies, freight brokers and other logistics operations. We are transitioning old-style operations to technology-advanced logistics entities and help them to grow their businesses. ELDs (electronic logging devices), fleet tracking and management 2.0 combined with AI-powered dispatch tools.











It’s a scenario every trucker dreads: you’re pulled in for a roadside inspection, the officer asks to see your logs, and your ELD won’t connect. You’re staring at a spinning wheel on your screen, trying to explain that your logs

Truckers who integrate all in one ELD fleet management systems to their businesses can significantly improve their operations by achieving compliance with the elog law while optimizing essential workflows. These systems streamline processes such as route planning, dispatch, vehicle maintenance,

When it comes to electronic logging devices, selecting the right provider can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and compliance. If your current provider falls short in areas such as customer support, user experience, or overall reliability, switching to a better