Electronic logging devices were designed to replace the traditional paper logbooks and automatic on-board recording devices previously used by commercial drivers to keep track of their hours of service. Since the implementation of the ELD mandate, elogs have become an essential part of truckers’ workflows. The law aims to impose a stricter control over commercial operators’ working hours. So, how do electronic logbooks work? To record data effectively, an e logbook for truckers must be synchronized directly with a vehicle’s engine.
It tracks information about the vehicle’s movement, including the time spent driving, the distance traveled, and the speed at which the vehicle is moving. These metrics are stored in the device and transferred to the app and online portal to be accessed by authorized personnel, such as drivers, fleet managers, and law enforcement officers. This article will examine the main issues related to compliance with federal logbook regulations and present a reliable elog provider to avoid costly penalties and delays in operations.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
Who Must Comply with Federal Logbook Regulations?
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) has made the use of electronic logging devices mandatory for most commercial motor vehicle drivers who are required to maintain records of duty status and whose vehicles are engaged in interstate commerce. Non-compliance may result in hefty fines and potential legal consequences. Therefore, it is crucial for motor carriers to have a clear understanding of federal logbook regulations and who can be exempt from them. Hours of service rules apply to drivers who operate CMVs that:
- Have a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) or gross combination weight rating (GCWR) of 10,001 pounds or more.
- Transport more than 8 passengers (including the driver) for compensation or 16 or more passengers (including the driver) not for compensation.
- Transport hazardous materials that require placarding.
Operators of these types of vehicles are required to record their hours of service using logs. While the ELD law requires most commercial vehicle drivers to utilize an e logbook for truckers, there are certain operators exempt from this rule, so they can their RODS on paper, including:
- Drivers who keep RODS for up to eight days within a 30-day period.
- Drive-away-tow-away drivers (where the driven vehicle is the actual commodity).
- Vehicles with engines manufactured before the year 2000.
It is important to note that state-specific requirements may apply in addition to federal regulations.
HOS247 Is a Leading Provider of E Logbook for Truckers
With a strong focus on reliability, safety, and efficiency, HOS247 offers a comprehensive solution for compliance with federal, interstate, and intrastate regulations. Our e logbook for truckers is designed to simplify the process of recording hours of service and producing RODS during roadside inspections, while providing many benefits to help motor carriers enhance productivity. Let’s examine the perks of the HOS247 system:
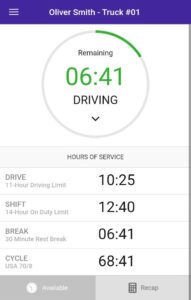
- Intuitive interface. Our software has a user-friendly interface that allows operators to effortlessly manage their logs, create electronic DVIRs, and to submit inspection reports in a few clicks. Additionally, the HOS247 web-based portal facilitates the work of fleet managers, providing easy access to the data gathered by the ELD and other driver and vehicle data to help streamline operations.
- Top-rated support. We pride ourselves on offering top-rated support and flexible customer policies. Independent user reviews indicate that clients value our service’s dependability and overall performance, along with the exceptional quality of our customer support. The HOS247 expert technical support team is available seven days a week to help customers with device usage and troubleshooting. Our multilingual experts speak Spanish and Russian in addition to English.
- Hardware and software compatibility. Our e-logbook is designed to work seamlessly with various truck types. Moreover, for driver convenience, the system can be effortlessly paired up with Android and iOS smartphones and tablets.
- Straightforward installation. The HOS247 device is easy to install and is ready to go on the road within minutes. This saves motor carriers from incurring additional costs on special installation or technicians, and prevents potential downtime.
- No-contracts. HOS247 employs a transparent and flexible system for client subscriptions, which can be adjusted monthly or yearly if needed without being tied into long-term contracts.
- Two-week trial. We provide a 14-day trial period, encouraging potential customers to test our system before subscribing to a plan. If, during this two-week period, the client determines that our electronic logbook is not suitable for their business needs, we offer a full refund.
- One-year warranty. HOS247 offers a highly durable hardware solution, specifically selected for its superior quality and reliability to prevent breakdowns while driving. In the event of any issues within the first year, we offer a free hardware replacement.
Do you have any questions? Talk to ELD Advisor: 650-405-3372 or Request Callback
Are Elog Apps FMCSA compliant?
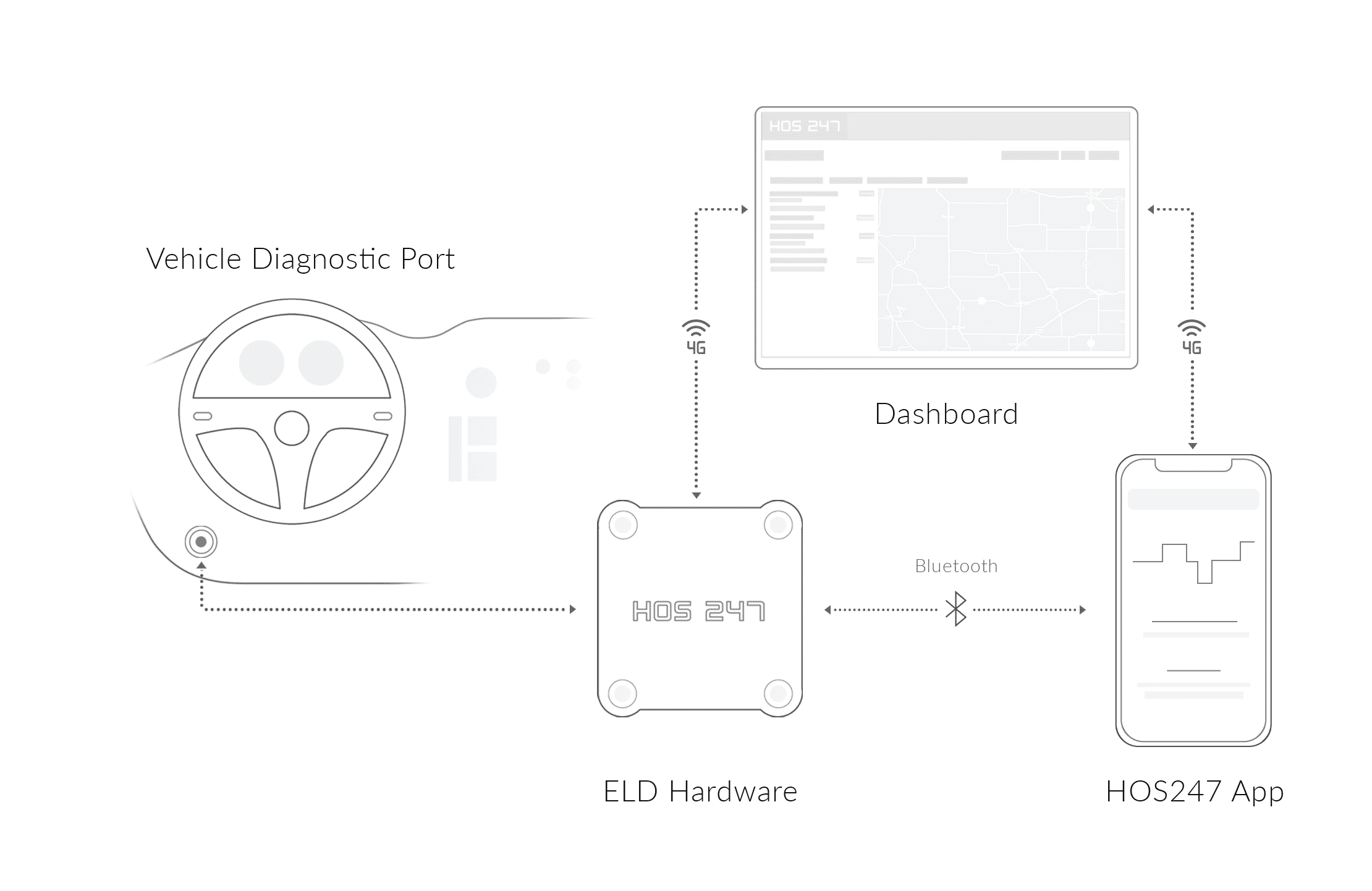
To comply with federal regulations and avoid costly fines, e logbooks for truckers must meet the mandatory technical requirements and be registered with the FMCSA. How do the ELD regulations apply to ELD apps? The Administration requires that the logging devices be connected to the engine and directly record driving time and other data. Therefore, although an app is an integral part of an electronic logging system as it displays the information that the engine-connected hardware records, the app alone cannot comply with the requirements of the mandate. Only when used with an FMCSA-approved tamper-resistant hardware device is this digital tool considered as compliant.
Can E Logbook Records Be Edited?
Another important compliance question is related to the editing of the data captured by the ELD logbook for truckers. Under what circumstances can a CMV driver edit an elog? According to FMCSA regulations, driving time can never be edited. However, authorized personnel or drivers can edit records in case of errors or missing information, following strict guidelines that require an annotation describing the reason for the change. These changes do not overwrite the previous information.

After editing, the driver must review, certify the accuracy, and resubmit the ELD log. Supervisory changes are not accepted until the driver confirms them with a signature, which is an important step that protects drivers from unauthorized alterations. If the driver is unavailable or chooses not to recertify the edit, it must be noted in the record. The carrier’s edit and annotation become part of the record, because drivers and motor carriers share responsibility for records of duty status integrity, and the original records are retained. As mentioned before, driving time cannot be changed to non-driving time, and the motor carrier must keep all records for at least six months.
Editing logs is a compliance issue that should be taken seriously because mistakes in the process may result in HOS violations. A user-friendly software can facilitate this and other tasks drivers must perform to stay compliant with the law. If you are looking for a reliable e logbook for truckers, we have a top-rated option for you.

As an expert in B2B and B2C sales, I’ve dedicated myself to perfecting sales processes and client retention strategies in the logistics and trucking industry. I have significantly contributed to the expansion of the ELD service, catering to retail and wholesale clients in need of HOS247 ELD solutions. My unwavering commitment to implementing state-of-the-art sales techniques and technologies ensures the continuous growth and success of businesses I work with.











Аrе drivers of pickups required to install ELDs? View ELDs for all types of vehicles > Many drivers of pickups are required to install and use ELD. Whether an ELD for pickup trucks is related to the gross vehicle weight

Аrе Drivers of OBD2 Vehicles Required to Install ELDs? ELDs work by synchronizing with the engine of a vehicle to record driving time for the more accurate and seamless recording of hours of service (HOS). Most electronic logging devices on

Electronic logging devices (ELDs) have changed how truck drivers track their hours on the road, replacing paper logs with digital records. For team drivers sharing the wheel, using ELDs comes with extra challenges that solo drivers don’t face. Team drivers